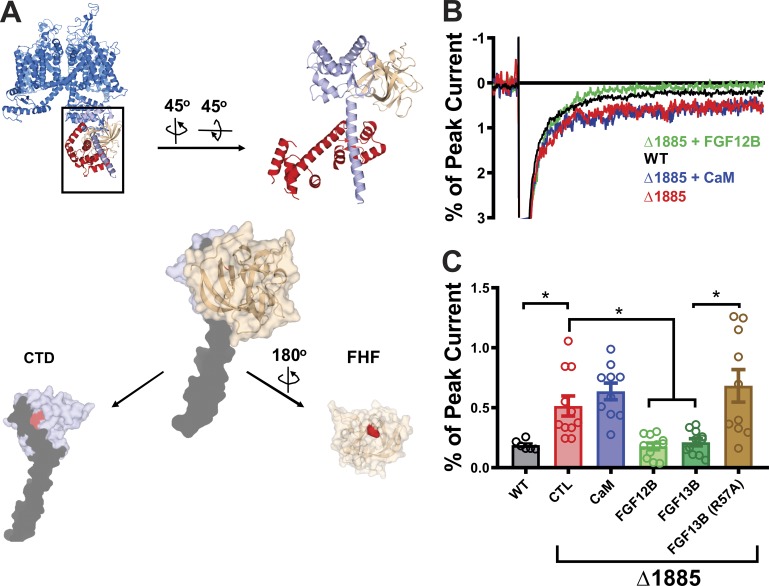
Figure 2.
FGF12B and FGF13B, but not CaM, are effective in rescuing persistent current in the Δ1885 mutant NaV1.5 channels. (A) Structure of the NaV1.5 CTD overlaid on NaVPas, with a zoomed-in view of the CTD (sky blue) along with CaM (red) and FGF13 (beige). The truncated protein in the Δ1885 mutant is shown in black. Below is the structure of the NaV1.5 CTD (blue), displaying the truncated portion in black, and the critical site for FHF binding in red (H1849), and the structure of FHF displaying the amino acid (R57) critical for the interaction with VGSC CTDs, shown in red. (B) Exemplar traces displaying the persistent currents in WT and mutant NaV1.5 channels. (C) Quantified data from WT and mutant NaV1.5 channels. *, P < 0.05. CTL refers to "control," i.e., no additional protein expressed.