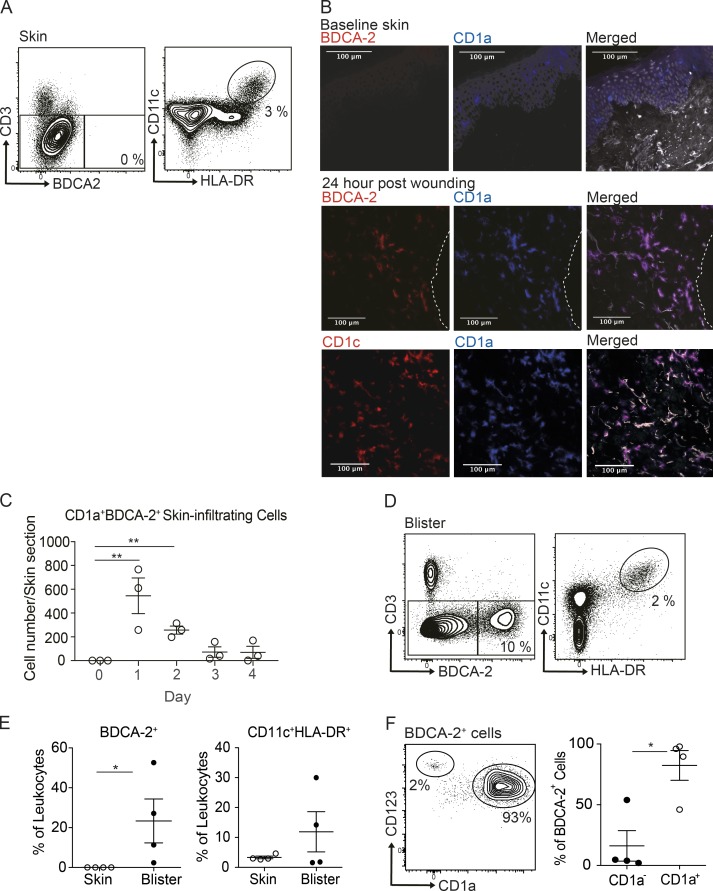
Figure 1.
CD1a-positive BDCA-2+ DCs can be found in the skin suction blisters and near skin wound. (A) Mononuclear cells isolated from normal skin were analyzed for DC subsets by flow cytometry. One representative result is shown of three independent experiments; n = 4. (B and C) Immunohistology of skin biopsies collected at day 0 to day 4 after bilateral skin wounds on the flank from healthy volunteers. The results of day 1 after wounding are shown (B). DAPI (gray), CD1a+ (blue), BDCA-2+ or CD1c+ (red), and CD1a+BDCA-2+ cells (purple). Dashed white lines represent the edge of the wound. One representative result is shown of three independent analyses. Time-course frequency of CD1a+BDCA-2+ DC per biopsy is shown (C). Each dot represents a biopsy. (D and E) Mononuclear cells isolated from skin suction blisters were analyzed for monocyte and DC subsets by flow cytometry. Percentages of BDCA-2+ DC and CD11c+HLA-DR+ cDCs/monocytes in the skin biopsies or blisters. (F) Expression of CD123 and CD1a by BDCA-2+ cells. Percentages of CD1a+ DCs and CD1a− DCs in the blisters. One representative blister result is shown of four independent experiments; each dot represents a donor. One to two blisters per challenge condition were created per upper arm of each donor. Scale bars, 100 µm. Lines represent the mean + SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; Student’s t test or one-way ANOVA.