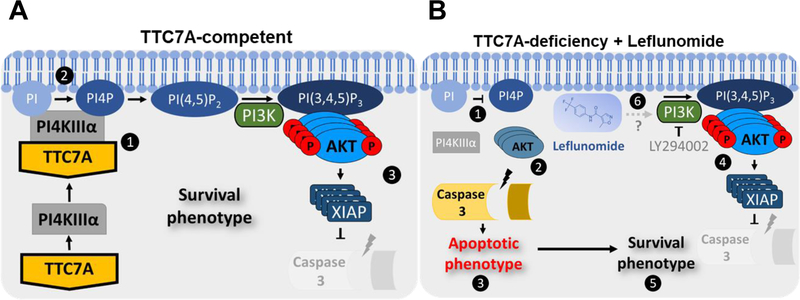
Figure 6. Model of leflunomide’s mechanism of action in TTC7A-deficiency.
(A) TTC7A-competent. 1, TTC7A binds and recruits PI4KIIIα to the plasma membrane. 2, PI4KIIIα phosphorylates PI lipids to create PI4P, precursor to PI (4,5)P2/ PI(3,4,5)P3. 3, PI3K phosphorylates PI (4,5)P2, required for AKT phosphorylation. p-AKT activates multiple downstream substrates that promote cell survival. For example, XIAP polyubiquitylates Pro Caspases 3,7, and 9 for proteasomal degradation, thereby reducing the susceptibility for Caspase-dependent cell death. (B) TTC7A-deficiency + leflunomide. 1, PI4KIIIα trafficking to (or kinase activity at) the plasma membrane is compromised in TTC7A-deficiency resulting in reduced PI4P. 2, Reduced p-AKT provides a rationale for increases in apoptosis. 3, Caspase-dependent apoptosis is frequently associated with TTC7A-deficiency. 4, Leflunomide treatment increases p-AKT and XIAP levels. 5, The apoptotic phenotype is ameliorated when TTC7A-deficient HAP1 cells are treated with leflunomide, suggesting a shift toward a survival phenotype. 6, It has yet to be established how leflunomide mediates p-AKT activation, however, PI3K-inhibition with LY294002 hinders leflunomide’s effect on AKT, XIAP, and Caspase 3 cleavage.