Figure 6.
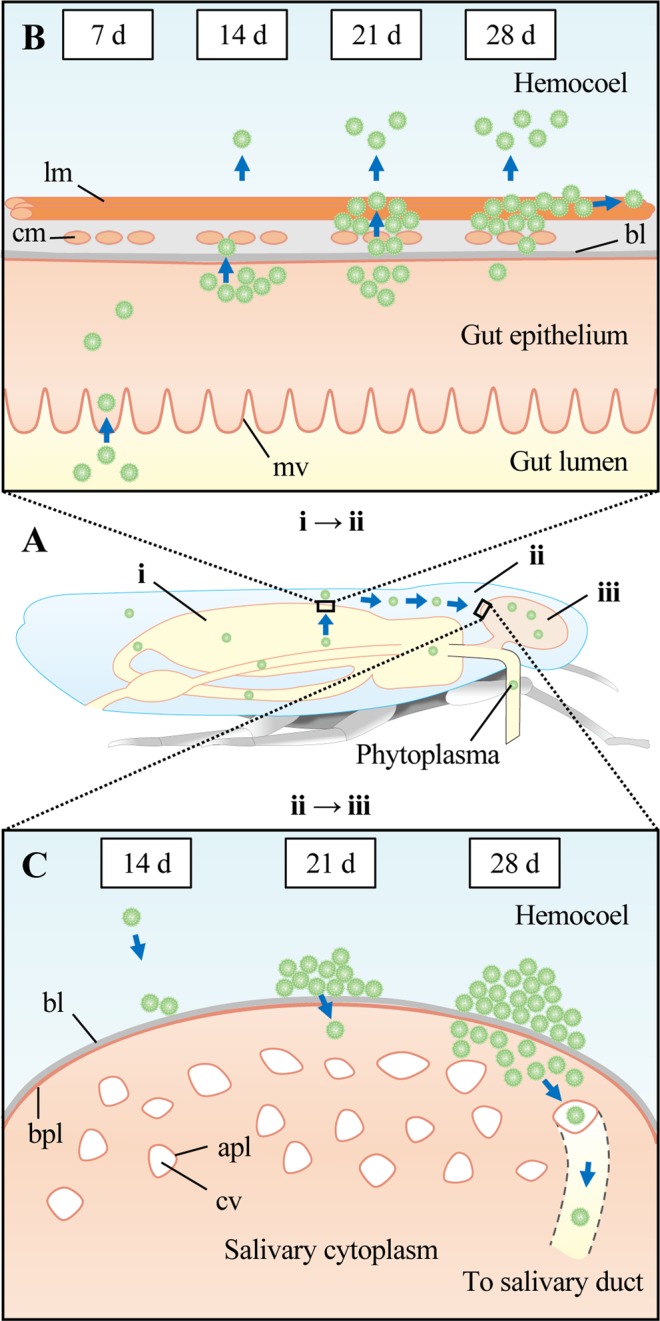
Proposed model of spatiotemporal dynamics of OY phytoplasma in its leafhopper vector, M. striifrons. (A) Dynamics of OY phytoplasmas in the entire insect body. OY phytoplasmas are acquired from plant phloem sap via the insect’s stylet. OY phytoplasmas enter the lumen of the alimentary canal (i), then pass through the canal into the hemocoel (i–ii). After circulating in the hemolymph, OY phytoplasmas finally reach the salivary glands (ii–iii). (B) Dynamics of OY phytoplasmas in the alimentary canal. By 7 days after acquisition start (daas; indicated as “d” in this figure), phytoplasmas enter the gut epithelium from the gut lumen through microvilli. At 14 daas, phytoplasmas multiply in the gut epithelium and move towards the basal lamina. Some phytoplasmas pass through the basal lamina to the internal circular muscle fibers and the hemocoel (i–ii). By 21 daas, many phytoplasmas cross the basal lamina to colonize both the internal circular muscle and external longitudinal muscle fibers and enter the hemocoel. At 28 daas, phytoplasmas mainly colonize the visceral muscles, spreading along muscle fibers. (C) Dynamics of OY phytoplasmas in salivary glands. A few phytoplasmas arrive at the basal lamina of the salivary gland cell at 14 daas (ii–iii). By 21 daas, many phytoplasmas accumulate on the surfaces of salivary gland cells; by 28 daas, some of these phytoplasmas enter into the cytoplasm. Thereafter, phytoplasmas in the cytoplasm pass through the apical plasmalemma of the salivary cavity and move into the salivary duct. mv, microvilli; bl, basal lamina; cm, circular muscle; lm, longitudinal muscle; bpl, basal plasmalemma; apl, apical plasmalemma; cv, cavity.
