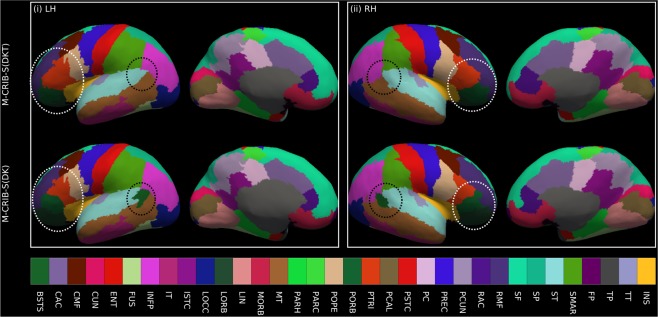
Figure 7.
Illustrative surface projections of the manual parcellation for one subject from the labelled set using the M-CRIB-S(DKT) and M-CRIB-S(DK) labels for left (LH) and right (RH) hemispheres. The ellipses highlight some differences between M-CRIB-S(DKT) and M-CRIB-S(DK). The white ellipses highlight location disagreements of the lateral orbitofrontal (LORB) and pars orbitalis (PORB) regions between atlases. The black ellipses encompass the banks of the superior temporal sulcus region, which is not present in the DKT. BSTS: Banks of the superior temporal sulcus, CAC: Caudal anterior cingulate, CMF: Caudal middle frontal, CUN: Cuneus, ENT: Entorhinal, FP: Frontal pole, FUS: Fusiform, INFP: Inferior parietal, INS: Insula, ISTC: Isthmus cingulate, IT: Inferior temporal, LIN: Lingual, LOCC: Lateral occipital, LORB: Lateral orbitofrontal, MORB: Medial orbitofrontal, MT: Middle temporal gyrus, PARH: Parahippocampal, PARC: Paracentral lobule, POPE: Pars opercularis, PORB: Pars orbitalis, PCING: Posterior cingulate, PCAL: Pericalcarine, POSTC: Posterior cingulate, PCUN: Precuneus, PREC: Precentral, PTRI: Pars triangularis, RAC: Rostral anterior cingulate, RMF: Rostral middle frontal, SF: Superior frontal, SMAR: Supramarginal gyrus, SP: Superior parietal, ST: Superior temporal gyrus, TP: Temporal pole, TT: Transverse temporal gyrus.