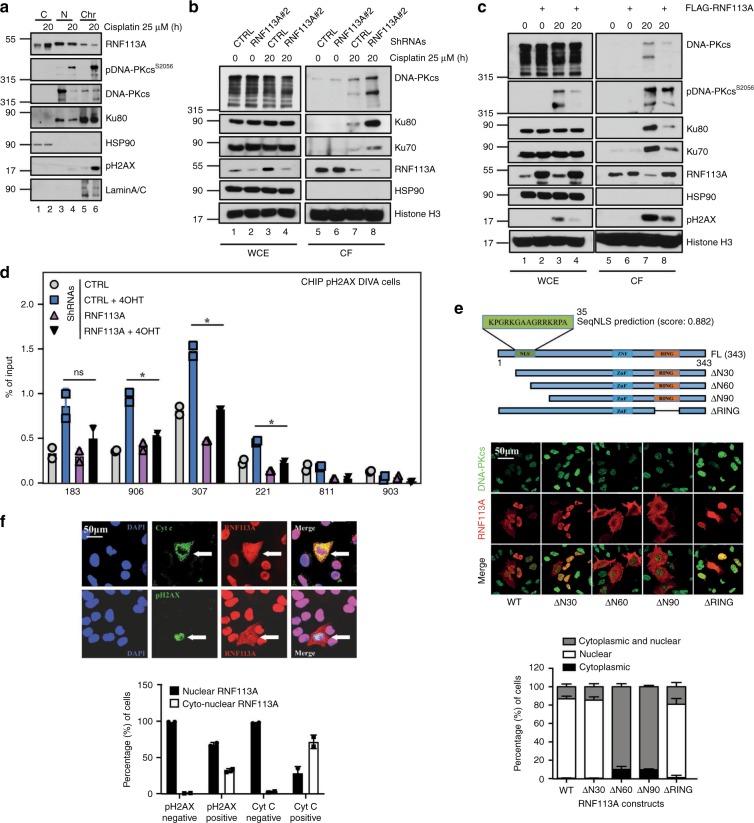
Fig. 3. RNF113A is recruited on DNA damage-induced foci.
a RNF113A is in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. A549 cells were treated or not with Cisplatin and WB analyses were carried out with cytoplasmic, nuclear and chromatin-enriched extracts. b, c RNF113A controls the recrutment of NHEJ factors on chromatin upon DNA damage. Control versus RNF113A-depleted A549 cells (b) or control versus RNF113A-overexpressing A549 cells (c) were treated or not with Cisplatin and WB analyses were carried out on chromatin fractions after pre-extraction with the CSK + RNase A buffer. d RNF113A controls the recruitment of pH2AX on DSBs. ChIP assays were conducted with extracts from control and RNF113A-depleted DIvA U2-OS cells treated or not with 4-hydroxy Tamoxifen (TAM). Primers 183, 906, 307, and 221 are pH2AX-associated AsiSI sites while primers 811 and 903 are non-associated and serve as negative control36. Immunoprecipitations using anti-IgG antibody served as negative control. The histogram shows recruitment of pH2AX on indicated sites. Results of two independent experiments (means ± SD, Student t-test, *p < 0.05) are shown. e A N-terminal nuclear localization signal (NLS) controls the nuclear import of RNF113A. The human RNF113A sequence was analyzed using the online NLS prediction algorithm SeqNLS (http://mleg.cse.sc.edu/seqNLS/) and the identified NLS (residues 21–35) is shown in green with a possibility score of 0.882. The subcellular localization of RNF113A constructs was analyzed by immunofluorescence in A549 cells, using DNA-PKcs as a nuclear marker. The percentage of cells showing a cytoplasmic and/or nuclear localization of RNF113A constructs is illustrated in the histogram below. f RNF113A moves in the cytoplasm of apoptotic cells showing some DNA damage. Anti-RNF113A Immunofluorescence analyses were conducted in Cisplatin-treated A549 cells. Cells showing some DNA damage or undergoing cell apoptosis were identifed through anti-pH2AX and Cyt C stainings, respectively. The histogram show the percentage of cells showing a nuclear or a cytoplasmic and nuclear localization of RNF113A, depending on their status for pH2AX or for Cyt C.