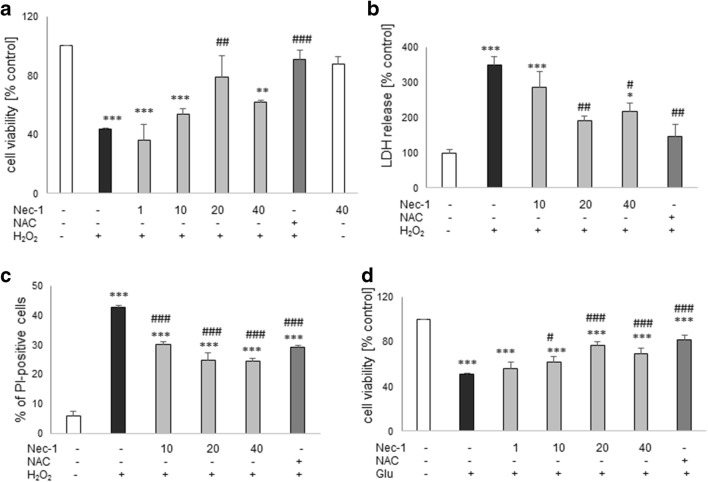
Fig. 4.
The effect of necrostatin-1 on H2O2- (a–c) or glutamate- (Glu, d) induced cell damage in hippocampal HT-22 cells. The cells were pre-treated for 30 min with necrostatin-1 (Nec-1; 1–40 μM) followed by 24 h of treatment with H2O2 (1 mM) or Glu (3 mM). As a positive control for the assays, we used antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC, 1 mM) which was given concomitantly with the cell damaging factors. a, d Results of cell viability assessment in the model of cell damage induced by H2O2- (a) and Glu (d) measured by the MTT reduction assay. Data were normalized to vehicle-treated cells (control) and are presented as the mean ± SEM from 3 to 10 separate experiments with 5 repetitions each. b Results of cell toxicity assessment in HT-22 cell exposed to H2O2 and Nec-1 measured by the LDH release assay. Data were normalized to vehicle-treated cells (control) and are presented as the mean ± SEM from 3 to 5 separate experiments with 5 repetitions each. c Flow cytometry results of propidium iodide (PI)-stained HT-22 cells after 24 h of cell treatment with H2O2 and Nec-1. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of PI-positive cells from 3 to 4 independent experiments with 2 replicates. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 vs. vehicle-treated cells; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, and ###P < 0.001 vs. H2O2- or Glu-treated cells