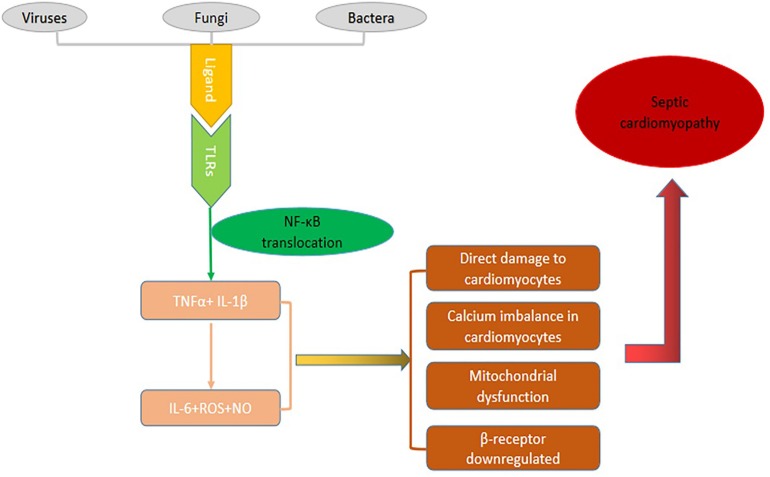
FIGURE 2.
The pathogenic mechanism of SCM. Specific components called ligands of viruses, bacteria or fungi bind to TLRs then go through a series of cascade reactions that cause NF-κB to be transcribed into the nucleus, causing the expression of inflammatory factor genes and producing a large number of inflammatory mediators. These inflammatory factors can cause a series of direct damage to cardiovascular dysfunction, disequilibrium of calcium homeostasis, mitochondrial dysfunction, down regulated expression of β adrenaline receptor, and eventually lead to cardiac dysfunction.