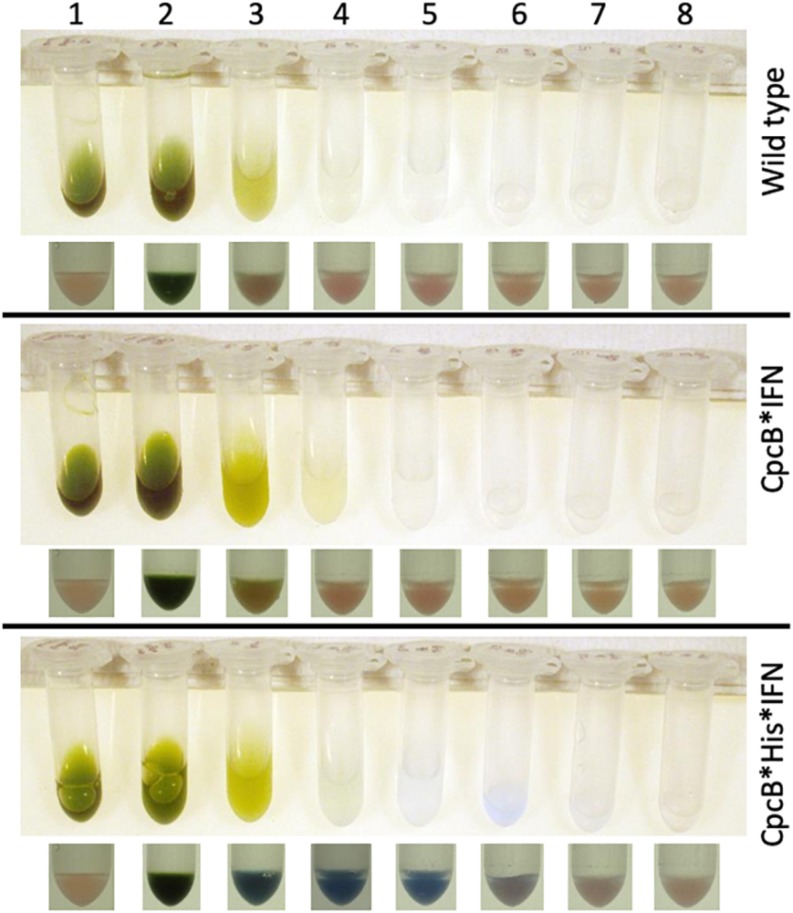
FIGURE 7.
Batch-scale purification of the recombinant CpcB∗His∗IFN protein through cobalt affinity chromatography. Protein purification was conducted employing a small amount of resin as solid phase. The latter was mixed and incubated with the cell extracts. The resin was pelleted and washed repeatedly with buffers containing imidazole at different concentrations. Lane 1 shows the cell extracts (upper panel) and the resin pellet (lower panel) of the wild type, CpcB∗IFN, and CpcB∗His∗IFN fusion construct cells prior to incubation with the resin. Note the natural pink coloration of the latter. Lane 2 shows the cell extracts (upper panel) and the resin pellet (lower panel) of the wild type, CpcB∗IFN, and CpcB∗His∗IFN fusion construct cells following a 5-min incubation with the resin in the presence of 10 mM imidazole. Note the blue coloration of the resin and the green coloration of the supernatant. Lanes 3–5 show the remaining cell extracts (upper panel) and the resin pellet (lower panel) of the wild type, CpcB∗IFN, and CpcB∗His∗IFN fusion construct cells following a consecutive wash of the resin three times with a buffer containing 10 mM of imidazole. Note the resulting clear supernatant and the pink coloration of the resin after the third wash (lane 5) for the wild type and CpcB∗IFN, suggesting absence of His-tagged proteins. Also note the blue coloration of the resin in the CpcB∗His∗IFN sample, which was retained in this pellet (lanes 3–5) in spite of the repeated wash, suggesting the presence of resin-bound blue-colored His-tagged proteins. Lanes 6–8 show the subsequent extracts (upper panel) and the resin pellet (lower panel) of the wild type, CpcB∗IFN, and CpcB∗His∗IFN fusion construct cells following a wash three times with a buffer containing 250 mM of imidazole, designed to dissociate His-tagged proteins from the resin. Note the bluish supernatant in lanes 6 and 7 and the corresponding loss of the blue color from the resin pellet, suggesting the specific removal of His-tagged proteins from the resin.