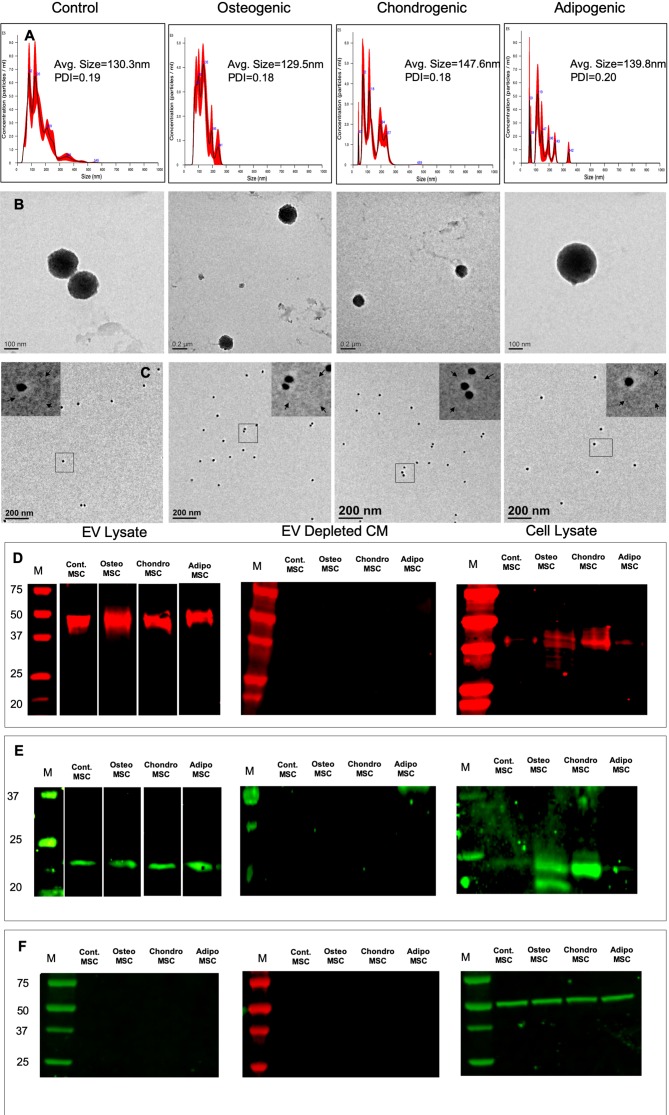
Figure 1.
Isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles (EVs): (A) Representative nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) plots of EVs isolated from naïve, osteogenic, chondrogenic, and adipogenic human mesenchymal stem cells (HMSCs). (B) Representative transmission electron microscopy images of the EVs isolated from naïve, osteogenic, chondrogenic, and adipogenic HMSCs. (C) Representative TEM images of Immunogold labeled (CD63, 20 nm gold particles) EVs from naïve, osteogenic, chondrogenic, and adipogenic HMSCs. The inserts in each of the images represent the boxed area. The arrows in the inserts point to EV membranes. (D) Immunoblot of EVs lysates, EV depleted conditioned medium, and cell lysates from naïve, osteogenic, chondrogenic, and adipogenic HMSCs for the presence of CD63 exosomal marker protein. (E) Immunoblot of EVs lysates, EV depleted conditioned medium, and cell lysates from naïve, osteogenic, chondrogenic, and adipogenic HMSCs for the presence of CD9 exosomal marker protein. (F) Immunoblot of EVs lysates, EV depleted conditioned medium, and cell lysates from naïve, osteogenic, chondrogenic, and adipogenic HMSCs for the presence tubulin.