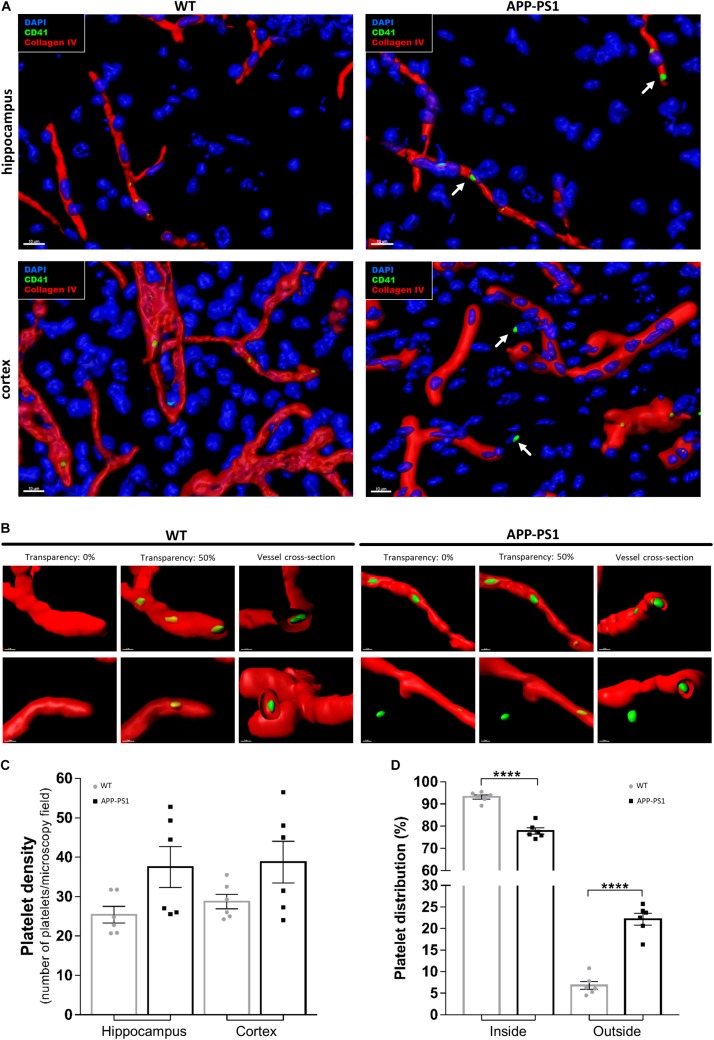
FIGURE 1.
Immunohistochemical analysis of platelet distribution in the brain of APP-PS1 mice. Brain sections from APP-PS1 mice and age-matched WT controls were stained with collagen IV (red) for blood vessels and CD41 (green) for platelets. 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride hydrate (DAPI; blue) was used as nucleus stain. Confocal microscopy images, from randomly selected hippocampal and cortical regions, were processed for 3D imaging. Platelets from WT and APP-PS1 mice were mainly located within the cerebral blood vessels (A,B), whereas platelets from APP-PS1 mice were frequently seen in the brain parenchyma or at the blood vessel wall, suggesting extravasation (A—arrows, B—right). Overall, APP-PS1 mice seem to have higher platelet densities in the hippocampus and cortex in comparison with WT controls (C). Moreover, quantification of platelets located inside (blood vessel) and outside (parenchyma/vessel wall) cerebral blood vessels revealed that APP-PS1 mice have a significantly higher percentage of platelets outside the blood vessels compared to WT controls (D). Data shown as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test (n = 6/group; including WT: six females and APP-PS1: three females and three males); ****p < 0.0001. Scale: 10 μm (A) and 3 μm (B).