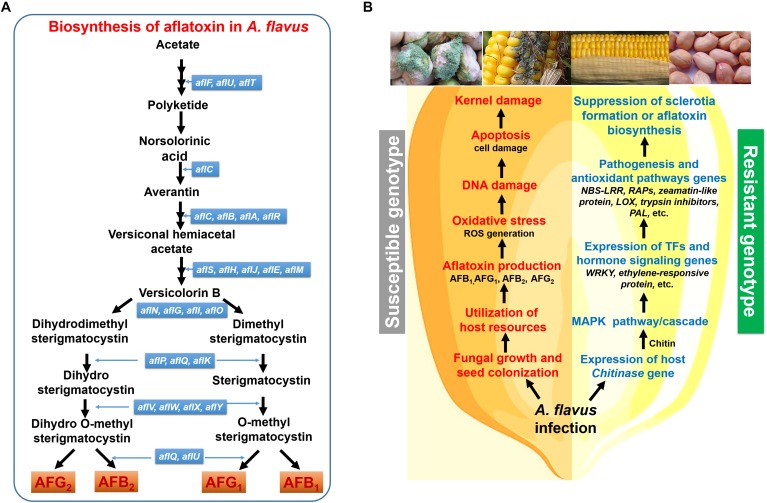
FIGURE 2.
A simplified representation of the aflatoxin biosynthesis pathway and the defense response mechanism in groundnut or maize. (A) Aflatoxin biosynthesis in A. flavus; (B) the aflatoxin biosynthesis pathway involve multiple genes which co-express together for the formation of toxin secondary metabolites. In the susceptible genotype infection leads to the A. flavus seed colonization and production of aflatoxin which causes suppression of host defense mechanism results in ROS generation and DNA damage causing cell death (apoptosis). In contrast, in resistant genotypes infection causes induction of host defense mechanism that include MAPK pathway which induces WRKY TF expression which is a key regulator of pathogenesis and antioxidant related genes involved in the suppression of aflatoxin biosynthesis pathway or detoxification of toxin.