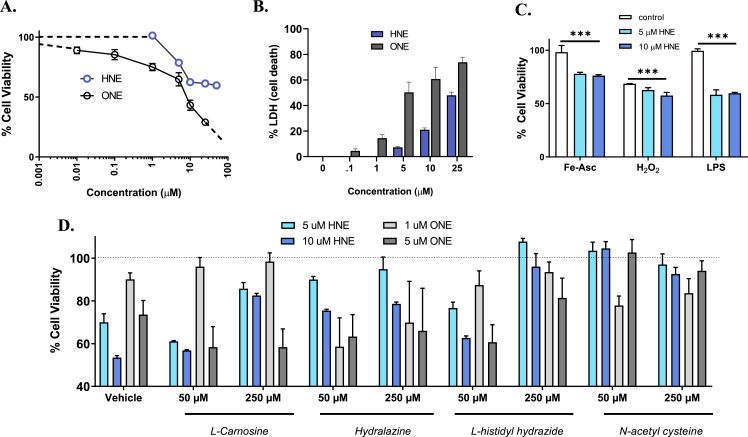
Fig. 2.
Oxidative stress induces neuronal loss and exacerbates stress response in vitro. (A and B) Cell viability of SH-SY5Y cells incubated with either HNE (0-50 μM) or ONE (0-25 μM) for 24 h with cell viability quantified by MTS (A) and LDH (B). (C) Cell viability of SH-SY5Y cells treated with either 5 or 10 μM HNE for 2 h and insulted with second neurotoxin for 24 h with cell viability normalized to HNE-treated cells and quantified by MTS. Concentrations for the neurotoxins were as follows: 50 μM iron ascorbate (Fe-Asc), 50 μM hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and 1 μg/mL lipopolysaccharide (LPS). (D) Cell viability of SH-SY5Y cells co-treated with well-studied scavengers (50 μM and 250 μM) and either HNE (5 μM and 10 μM) or ONE (1 μM and 5 μM) for 24 h with cell viability quantified by MTS. Data represent mean ± S.E.M. analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's or Tukey's multi-comparison analysis from three cell passages (n = 6/passage, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).