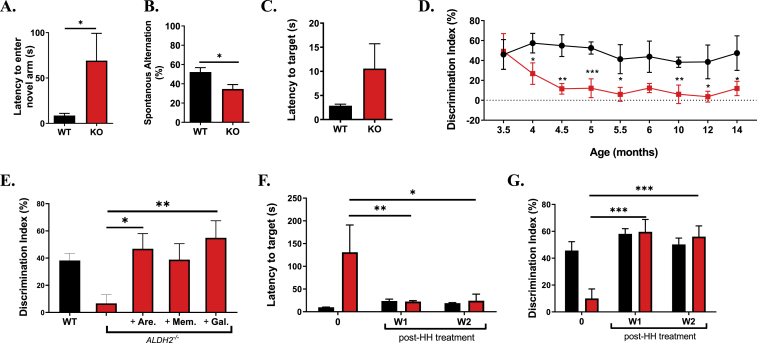
Fig. 3.
ALDH2−/− mice have a mild phenotype and exhibit mild cognitive impairment that is reversed by pro-cognitive agents. (A and B) Quantitative analysis of the performance of WT and ALDH2−/− mice in the Y-maze forced alternation (A) task which measures latency to enter a previously locked arm and the spontaneous alternation (B) task which measures the exploration of the arms available. (C) Quantitative analysis of the performance of WT and ALDH2−/− mice in the Barnes maze, which measures ability of mice to find a hidden target.(D) Quantitative analysis of the performance of WT and ALDH2−/− mice in the novel recognition (NOR) test, which measures recognition memory, from 3.5 through 10 months. (E). Cognitive performance of ALDH2−/− mice treated with 10 mg/kg Arecoline (Are), 20 mg/kg Memantine (Mem) or 10 mg/kg Galantamine (Gal) via i.p. 20 min prior to the familiarization phase in the NOR test, and tested for their DI% in the testing phase. (F and G) Quantitative analysis of the performance of 14 month old WT and ALDH2−/− mice in the Y-maze (F) and NOR (G) with daily treatment of 10 mg/kg i.p. L-histidyl hydrazide (HH). Pre-testing (0) was measured prior to beginning treatment. Unless otherwise indicated, all behavior studies were performed on 9 month old mice. Data represent mean ± S.E.M analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's or Tukey's multi-comparison analysis from (n = 6–8 mice/group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.