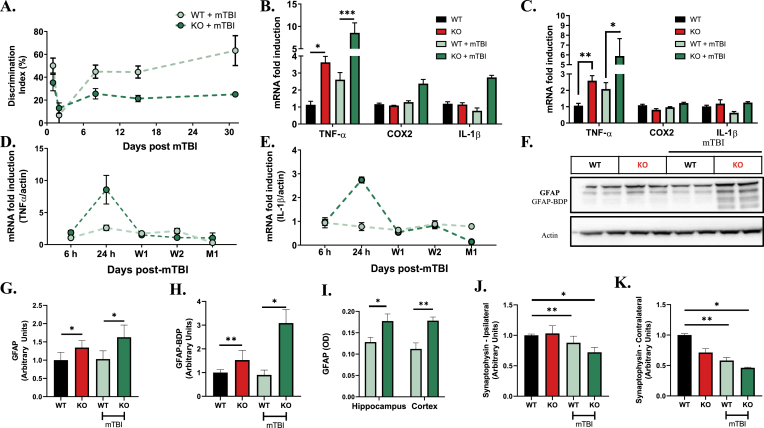
Fig. 6.
mTBI induces exacerbated acute and chronic neuroinflammation and sustained cognitive deficits in the Aldh2−/− mice. (A) Quantitative analysis of the performance of WT and ALDH2−/− mice with mTBI or null controls in NOR for 1, 7, 14 and 30 days post-mTBI injury. (B and C) qRT-PCR analysis of TNF-α, COX2 and IL-1β gene expression in the ipsilateral (B) and contralateral (C) hemispheres of WT and ALDH2−/− mice 24 h post-mTBI and null mouse controls. (D and E). qRT-PCR analysis of TNF-α (D) and IL-1β (E) of WT and ALDH2−/− mice 6 h, 24 h, 1 week (W1), 2 weeks (W2) and 1 month (M1) post-mTBI and null mouse controls. (F–H) Representative immunoblot of WT and ALDH2−/− mice 24 h post-mTBI and null controls probed with GFAP Ab (F) with quantitative analysis of GFAP (50 kDa, G) and GFAP-mediated breakdown products (35–45 kDa, GFAP-BDP, H). (I) Quantitative analysis of brain slices of WT and ALDH2−/− mice 24 h post-mTBI probed with GFAP Ab in optical density units. (J and K) Quantitative analysis of immunoblots from the ipsilateral (J) and contralateral (K) hemispheres of WT and ALDH2−/− mice 24 h post-mTBI and null controls probed with synaptophysin Ab (42 kDa). All samples were normalized to the housekeeping gene, β-actin. Data represent mean ± S.E.M analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's or Tukey's multi-comparison analysis from (n = 6) *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.