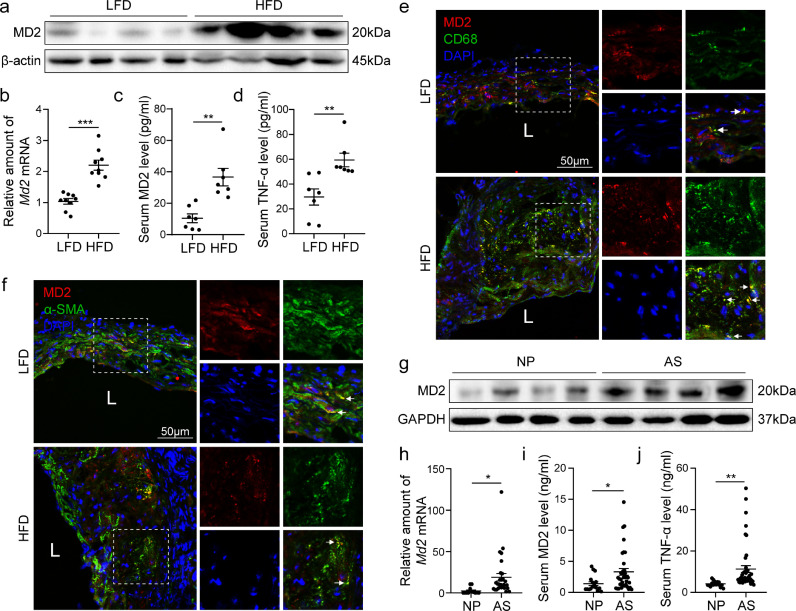
Fig. 1.
MD2 is elevated in atherosclerotic lesion macrophages. (a) MD2 protein levels in aortas of Apoe−/− mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD) or normal/low-fat diet (LFD) were detected by western blotting. β-actin was used as loading control. Representative immunoblots were shown. (b) mRNA levels of Md2 in aortic sinus of Apoe−/- mice fed with LFD and HFD [n = 9]. (c, d) Serum levels of soluble MD2 protein (c) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α; d) in Apoe−/− mice fed with LFD and HFD [n = 7]. (e, f) Representative immunofluorescence staining of MD2 (red, e and f), macrophage marker CD68 (green, e), and smooth muscle cell marker α-SMA (green, f). Tissues were counterstained with DAPI (blue). White arrows indicate co-location of MD2 and CD68 (e) or α-SMA (f) staining [scale bar = 50 μm]. (g) Western blot analysis of MD2 protein levels in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (hPBMCs) isolated from patients with atherosclerosis (AS) and without AS (normal peoples, NP). (h) mRNA levels of Md2 in hPBMCs. (i, j) Serum levels of MD2 protein (i) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α; j) in hPBMCs isolated from AS [n = 40] and NP [n = 15]. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)