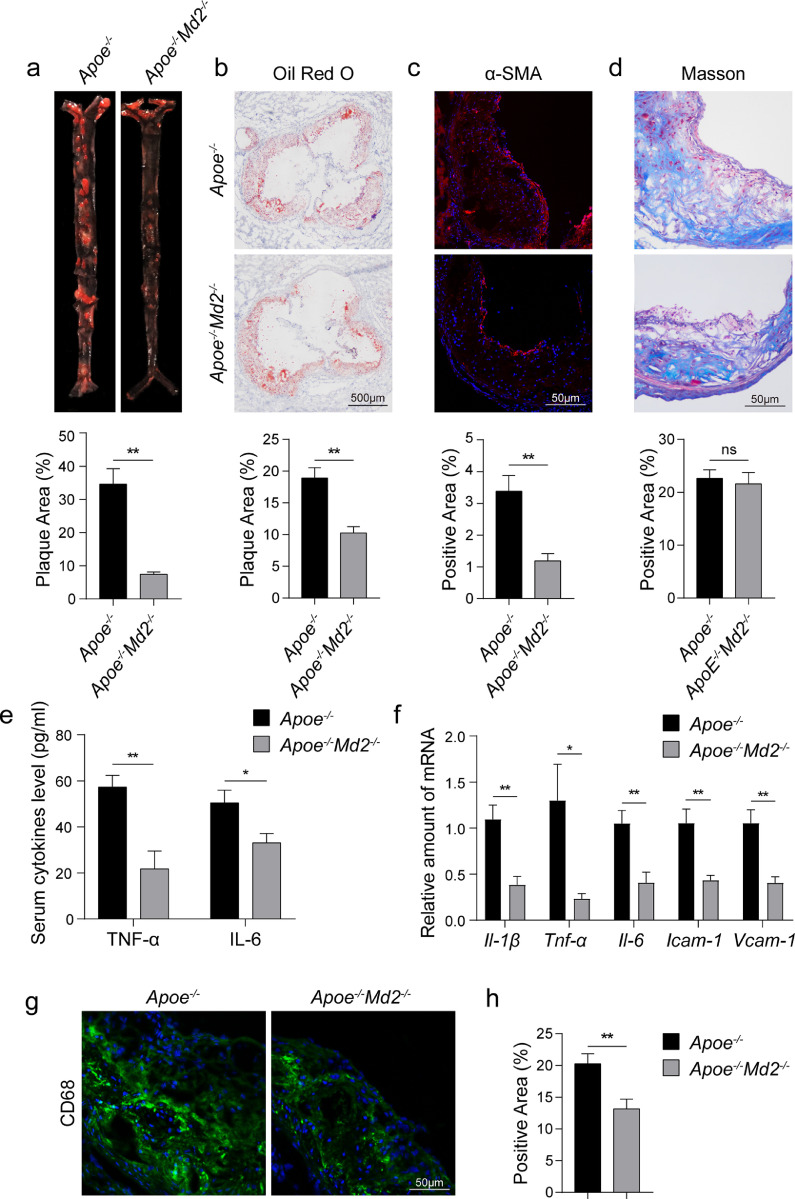
Fig. 2.
MD2 deficiency reduces atherosclerosis in HFD-fed ApoE−/− mice. (a) En face Oil Red O staining of aortas from Apoe−/− and Apoe−/−Md2−/− mice fed a HFD for 16 weeks. Oil Red O staining highlighting neutral lipids (red). Lower panel showing quantification of plaque lesion area from Oil Red O staining. Plaque area was defined as percentage of total surface area of the aorta [n = 6]. (b) Oil Red O staining of aortic sinus. Lower panel showing quantification of lesion area highlighted by Oil Red O staining [n = 6; scale bar = 500 μm]. (c) Representative images of α-SMA (red) staining of aortic sinus. Lower panel showing quantification of α-SMA staining area [n = 6; scale bar = 50 μm]. (d) Representative images of Masson's Trichome staining for collagen deposition. Lower panel showing quantification of fibrotic area [n = 6; scale bar = 50 μm]. (e) Serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 in mice fed a HFD [n = 10]. (f) mRNA analysis of proinflammatory cytokines (Il-1β, Tnf-α, Il-6) and adhesion molecules (Icam-1, Vcam-1) in aortic sinus [n = 6]. (g) Representative immunofluorescence staining images for CD68 (green) in aortic sinus. Tissues were counterstained with DAPI (blue) [scale bar = 50 μm]. (h) Quantification of CD68-positive area in aortic sinus slices [n = 6]. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)