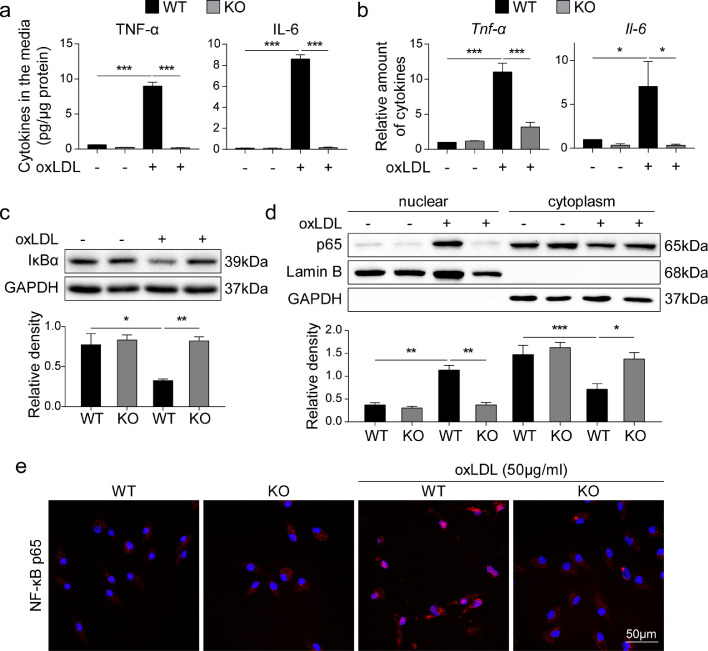
Fig. 4.
MD2 mediates ox-LDL-induced proinflammatory cytokine production and NF-κB activation (a) Primary macrophages isolated from Md2−/− (KO) and wildtype (WT) mice were challenged with 50 μg/mL ox-LDL for 24 h. Levels of TNF-α and IL-6 cytokines in culture media were measured by ELISA and reported as pg/μg protein [n = 6]. (b) mRNA levels of Tnf-α and Il-6 in macrophages isolated from KO and WT mice. Cells were exposed to 50 μg/mL ox-LDL for 6 h [n = 4]. (c) Levels of IκB in the primary macrophages exposed to 50 μg/mL ox-LDL for 30 min. GAPDH was used as loading control. Lower panel showing densitometric quantification [n = 4]. (d) Immunoblot detection of NF-κB p65 subunit in cytosolic and nuclear fractions prepared from cells exposed to 50 μg/mL ox-LDL for 30 min. Lamin B and GAPDH were used as loading control for nuclear and cytosolic proteins, respectively. Lower panel showing densitometric quantification [n = 4]. (e) Immunofluorescence staining for NF-κB p65 subunit (red) in primary macrophages exposed to ox-LDL for 1 h. Cells were counterstained with DAPI (blue) [scale bar = 50 µm]. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)