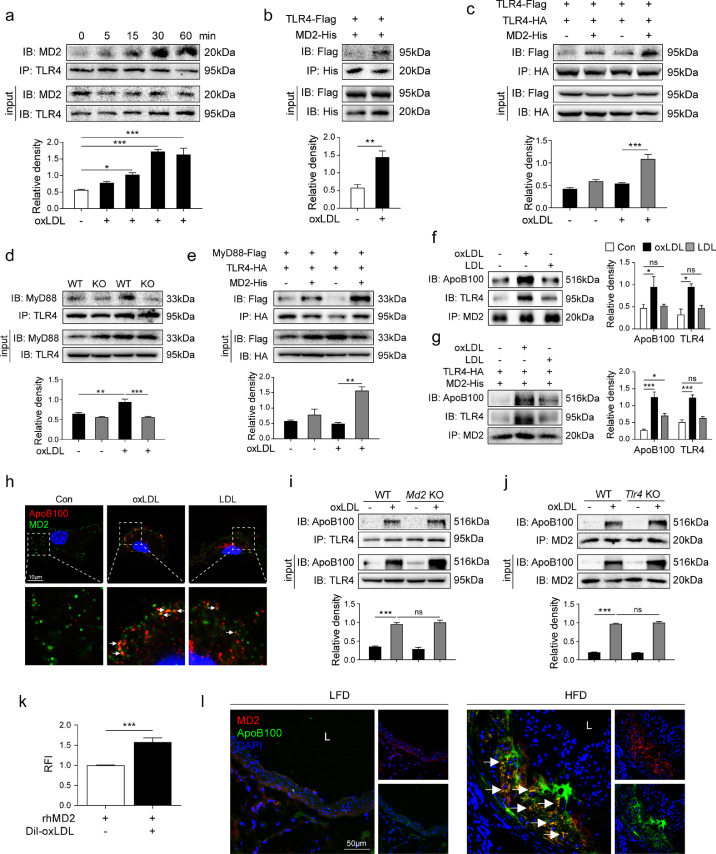
Fig. 5.
MD2 is essential for ox-LDL-induced TLR4 dimerization and activation via direct interaction with ox-LDL (a) Macrophages from wildtype mice were incubated with 50 µg/mL ox-LDL for indicated time periods. TLR4 was immunoprecipitated (IP) and MD2 was detected by immunoblotting (IB). Lower panel showing the densitometric quantification of MD2-TLR4 association [n = 4]. (b) Interaction between MD2 and TLR4 was confirmed by co-immunoprecipitation assay in HEK-293T cells transfected with MD2-His and TLR4-Flag expressing plasmids. Lower panel showing the densitometric quantification [n = 4]. (c) Dimerization of TLR4 was assessed by co-immunoprecipitation assay in HEK-293T cells transfected with Flag- and HA-tagged TLR4 and His-tagged MD2 plasmids. Cells were exposed to 50 µg/mL ox-LDL for 30 min. Samples were immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-HA followed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-Flag. Lower panel showing the densitometric quantification. [n = 4]. (d) Primary macrophages from wildtype (WT) mice and MD2−/− mice (KO) were incubated with 50 µg/mL ox-LDL for 30 min. TLR4 was immunoprecipitated (IP) and MyD88 was detected by immunoblotting (IB). Lower panel showing the densitometric quantification [n = 4]. (e) Interaction between MyD88 and TLR4 was detected by co-immunoprecipitation assay in HEK-293T cells transfected with TLR4-HA, MyD88-Flag, and MD2-His expressing plasmids. Cells were treated with or without 50 µg/mL ox-LDL for 30 min. Lower panel showing the densitometric quantification [n = 3]. (f) Macrophages isolated from wildtype mice were exposed to 50 μg/mL ox-LDL or LDL for 30 min. Interaction between ApoB100, MD2, and TLR4 was assessed by co-immunoprecipitation. Right panel showing the densitometric quantification [n = 3]. (g) Interaction between ApoB100, MD2, and TLR4 was detected by co-immunoprecipitation in HEK-293T cells transfected with TLR4-HA and MD2-His expressing plasmids. Cells were treated with or without 50 µg/mL ox-LDL for 30 min. Right panel showing the densitometric quantification [n = 4]. (h) Primary macrophages were treated with 50 µg/mL ox-LDL or LDL, and then were stained for MD2 (green) and ApoB100 (red). DAPI (blue) was used to counterstain. Lower panels show higher magnification. (i) Macrophages isolated from wildtype (WT) and Md2−/− (Md2KO) mice were incubated with 50 µg/mL ox-LDL for 30 min. Interaction between TLR4 and ApoB100 was assessed by co-immunoprecipitation. Lower panel showing the densitometric quantification [n = 3] (j) Macrophages isolated from WT and Tlr4−/− (Tlr4KO) mice were incubated with 50 µg/mL ox-LDL for 30 min. Interaction between MD2 and ApoB100 was assessed by co-immunoprecipitation. Lower panel showing the densitometric quantification [n = 3]. (k) The interaction between MD2 and ox-LDL was determined using a cell-free assay. rhMD2 was immobilized and DiI-labeled ox-LDL was added. Binding was determined by relative fluorescence intensity (RFI), normalized to blanks without rhMD2 immobilization [n = 4]. (l) Representative immunofluorescence staining of MD2 (red) and ApoB100 (green) in aortic sinus of Apoe−/− mice maintained on HFD. Tissues were counterstained with DAPI (blue) [scale bar = 50 μm]. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)