Figure 2.
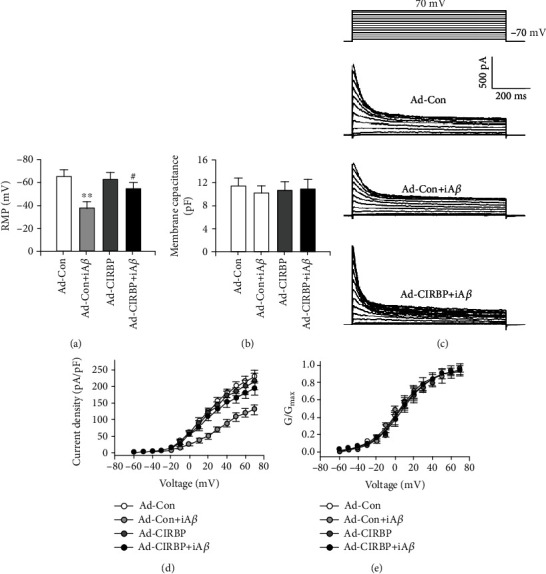
CIRBP reversed iAβ-induced electrophysiological changes that are responsible for neuronal toxicity. (a, b) Resting membrane potentials (RMP) (a) and membrane capacitance (b) were recorded among different groups. ∗∗p < 0.01vs. Ad-Con, #p < 0.05vs. Ad-Con+iAβ. (c) Typical recordings of whole-cell K+ current in the Ad-Con, Ad-Con+iAβ, and Ad-CRIPB+iAβ groups by depolarizing the membrane from -70 mV to +70 mV from a holding potential at -70 mV with 10 mV increasing steps. (d) Current-voltage relationship of the peak K+ current density. ∗∗p < 0.01vs. Ad-Con. (e) Voltage-dependent activation curve of K+ current showing there was no difference among different groups.
