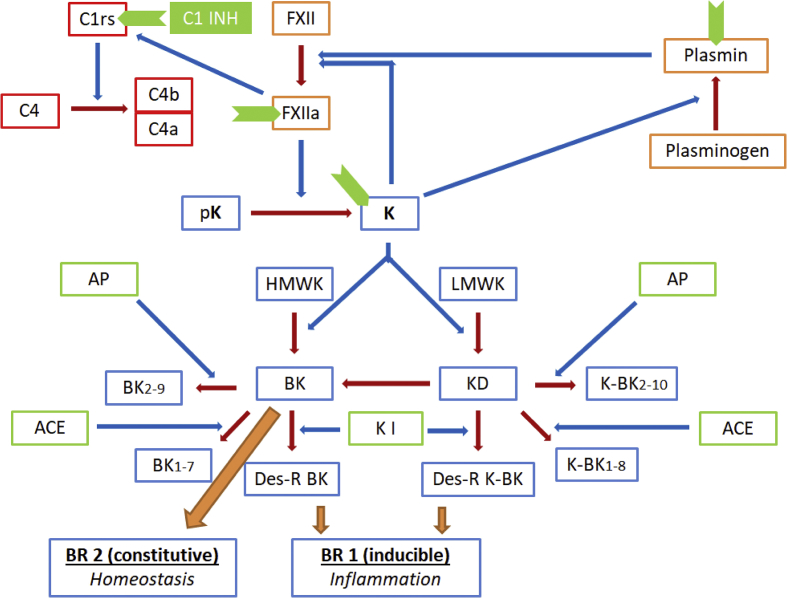
Figure 1.
A simplified summary of the kinin metabolism and the mutual interactions between the kinin, complement, hemostatic and fibrinolytic pathways. (The blue arrows represent the augmentation of the enzymatic reactions shown in brown arrows). The sites of action of C1 esterase inhibitor (C1-INH) are represented in green chevron shapes). Abbreviations: FXII – Factor XII, a as a suffix indicates the active form; pK – prekallikrien; K (in bold) – kallikrien; HMWK – high molecular weight kininogen; LMWK – low molecular weight kininogen; BK – bradykinin; KD – kallidin (lysine-bradykinin: K-BK), BK2-9 – bradykinin with its first amino acid cleaved off; BK1-7 – bradykinin with its last two amino acids cleaved off; Des-R BK – bradykinin with its ninth arginine residue cleaved off; meaning of subscripts in case of kallidin (K-BK) is the same as that for bradykinin derivatives; ACE (also called kininase II) – angiotensinogen converting enzyme, AP – aminopeptidase, K I – kininase I.