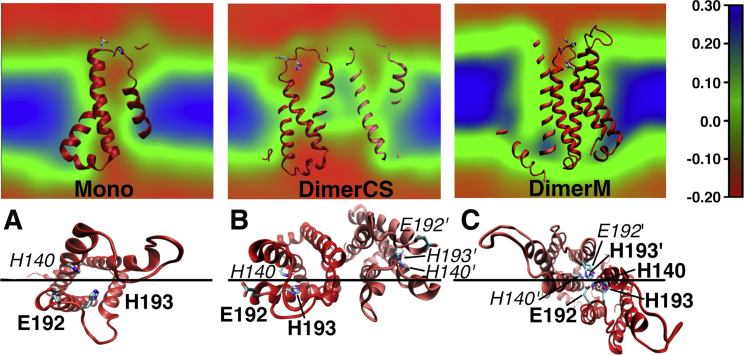
Figure 6.
Electrostatic potential maps (EPMs) of (A) the monomer (Mono) and dimers (B) DimerCS, and (C) DimerM. The potential is shown in a plane through the membrane that goes between H140 and H193 side chains as depicted by the black line in the lower panel. In the lower panel, the channels are seen from the extracellular (foreground) to the intracellular (background) sides of the membrane. The residues visible in front of the EPMs in the upper panel are labeled in bold in the lower panel, whereas those located behind the EPMs are labeled in italics. Color coding in the EPMs is shown on the right (in volts). EPMs are averaged over the five MD simulations for each HV1 structure. The attractive potential (red) in the interior of the channels is disrupted from the bulk solution in Mono and in DimerCS but continuous between the bulk solution and the dimer interface of DimerM, funneling the zinc cations toward the binding sites.