Fig. 4. ACKR3 binding kinetics and arrestin recruitment of CXCL12 mutants.
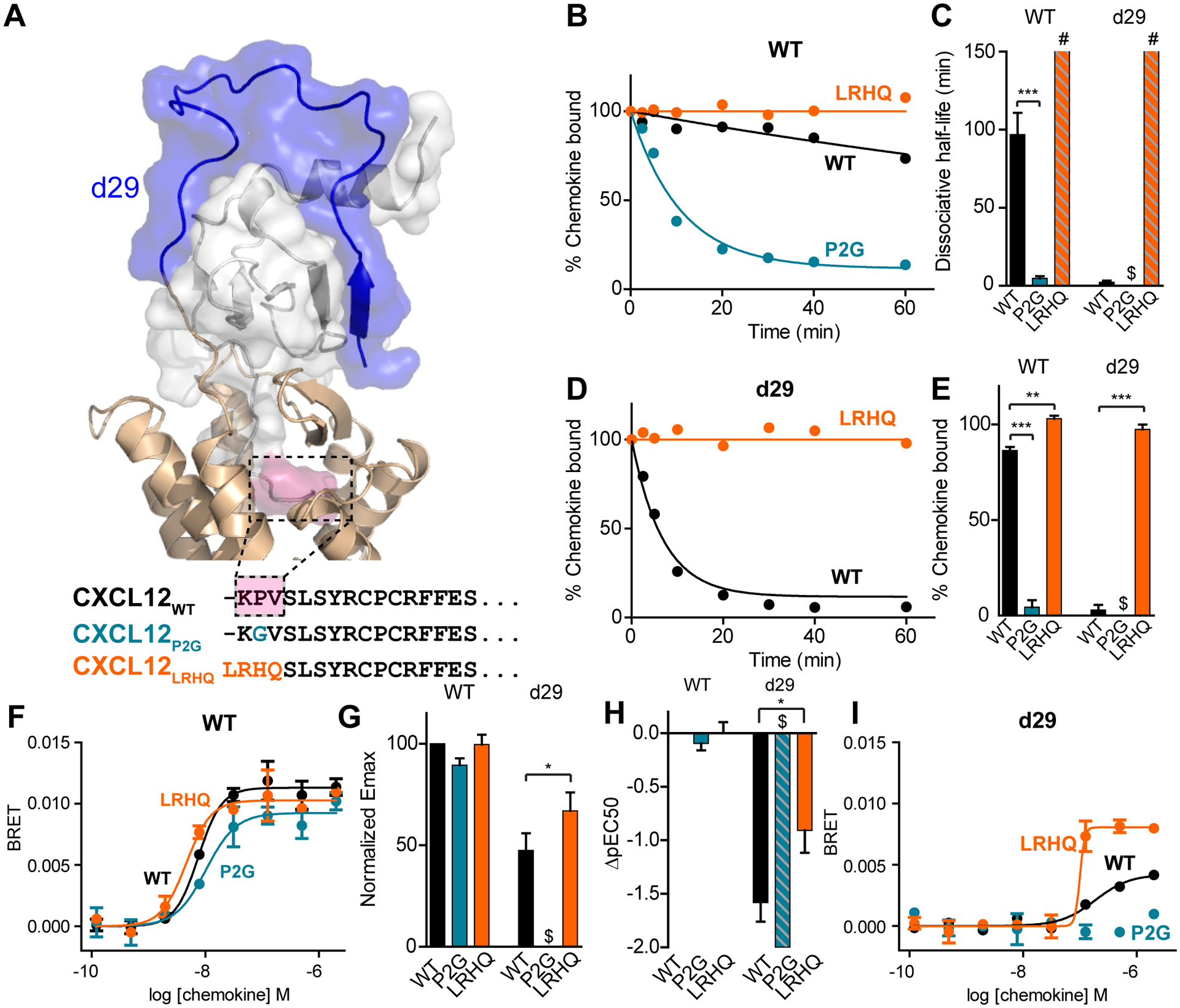
(A) Extracellular portion of ACKR3:CXCL12 model and N-terminal sequences of CXCL12 variants. Residues in CXCL12WT that differ between the three mutants are highlighted in pink in the model. (B) Representative curves for CXCL12 dissociation from bril-ACKR3WT detected by flow cytometry. (C) Means and standard errors from three or more experiments of dissociative half-lives determined from fitting dissociation curves to a single exponential. The dissociative half-life of CXCL12LRHQ was too slow to quantify but was estimated to be longer than 150 min (highlighted by # in figure). Binding of CXCL12P2G to ACKR3d29 was too low to quantify a dissociation rate (highlighted by $ in figure). (D) Representative CXCL12 dissociation curves from bril-ACKR3d29 detected by flow cytometry. (E) Means and standard errors of the percent specific chemokine binding remaining 20 min after the start of dissociation for three or more experiments. CXCL12LRHQ has a higher fraction of chemokine bound than CXCL12WT for both bril-ACKR3WT and bril-ACKR3d29 and CXCL12P2G has a lower fraction bound for bril-ACKR3WT. Binding of CXCL12P2G to ACKR3d29 was too low to quantify (highlighted by $ in figure). (F) Representative dose-response curves for β-arrestin-2 recruitment to ACKR3WT and ACKR3d29. (G) Emax normalized to ACKR3WT with CXCL12WT (%Emax =Emax,mutant/Emax,WT × 100). Each bar represents the average and standard errors of three or more experiments. (H) Mean and standard errors of pEC50 relative to ACKR3WT with CXCL12WT (ΔpEC50=pEC50,mutant-pEC50,WT). CXCL12P2G-mediated recruitment of arrestin to ACKR3d29 was barely detectable and the ΔpEC50 was estimated to be less than −2 (highlighted by $ in G and H). (I) Representative dose-response curves for β-arrestin-2 recruitment to ACKR3WT and ACKR3d29. Significant differences for CXCL12P2G and CXCL12LRHQ compared to CXCL12WT are noted: *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 from one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test.
