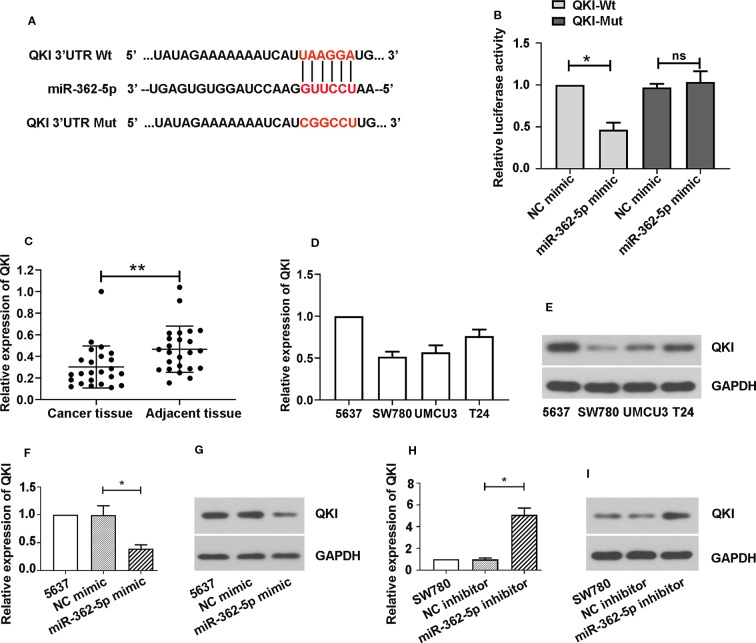
Figure 3.
MiR-362-5p directly targets with QKI. (A) The predicted binding sites within miR-362-5p and wild-type of 3′UTR of QKI (QKI-Wt) and the mutant sequence of 3′UTR of QKI (QKI-Mut). (B) The pmirGLO luciferase vector was inserted with fragments of QKI-Wt or QKI-Mut. Then the constructed pmirGLO luciferase vectors (1 μg) were co-transfected with miR-362-5p mimic (50 pmol) or NC mimic. Luciferase reporter assay was performed after for 48 h transfection. *p < 0.05 vs. NC controls. (C) The relative expression levels of QKI in bladder cancer tissues (N=24) and adjacent tissues (N=24) were analyzed by qRT-PCR. **p < 0.01 vs. adjacent tissues. (D, E) The mRNA and protein expression levels of QKI in bladder cancer cell lines 5637, SW780, UMUC3, and T24 were analyzed by qRT-PCR. (F, G) The 5637 cells were transfected with miR-362-5p mimic (100 pmol) or NC mimic for 48 h. The mRNA and protein levels of QKI were detected by qRT-PCR and western blot. (H, I) The SW780 cells were transfected with miR-362-5p inhibitor (100 pmol) or NC inhibitor for 48 h. The mRNA and protein levels of QKI were detected by qRT-PCR and western blot. The expression was displayed as fold of 5637 or SW780 cells. GAPDH was used as an internal control in western blot. *p < 0.05 vs. corresponding controls.