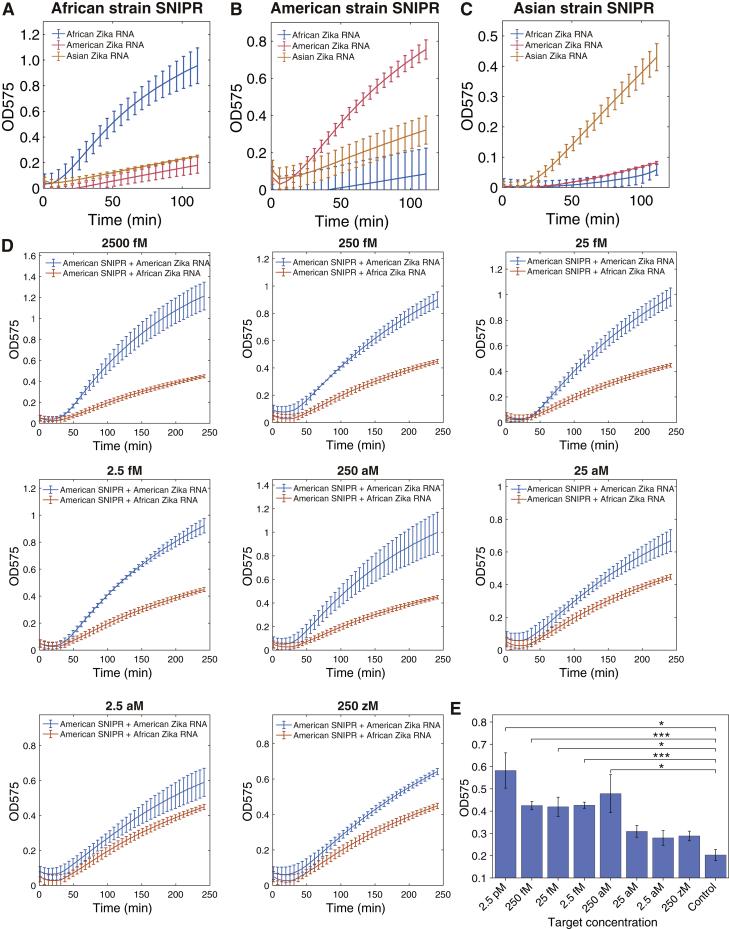
Figure S6.
Detection of Zika Virus RNA, Related to Figure 6
(A-C) Time-course measurements of strain-specific Zika SNIPRs. SNIPRs challenged with RNA from three different strains of Zika. (n = 3 technical replicates; bars represent arithmetic mean ± SD)
(D) Time-course measurements of the OD575 signal change for different starting concentrations of Zika RNA in paper-based cell-free reactions. The Zika RNA fragments were amplified using RT-RPA reactions at starting concentrations ranging from 250 zM to 2.5 pM. (n = 3 technical replicates; bars represent arithmetic mean ± SD)
(E) OD575 measured for different Zika RNA concentrations after 100 minutes of paper-based cell-free reactions with the SNIPR for the American Zika strain. Concentrations of 250 aM or higher provide p < 0.05 and a visible purple color (OD575 > ∼0.4). (n = 3 technical replicates; two-tailed Student’s t test; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; bars represent arithmetic mean ± SD)