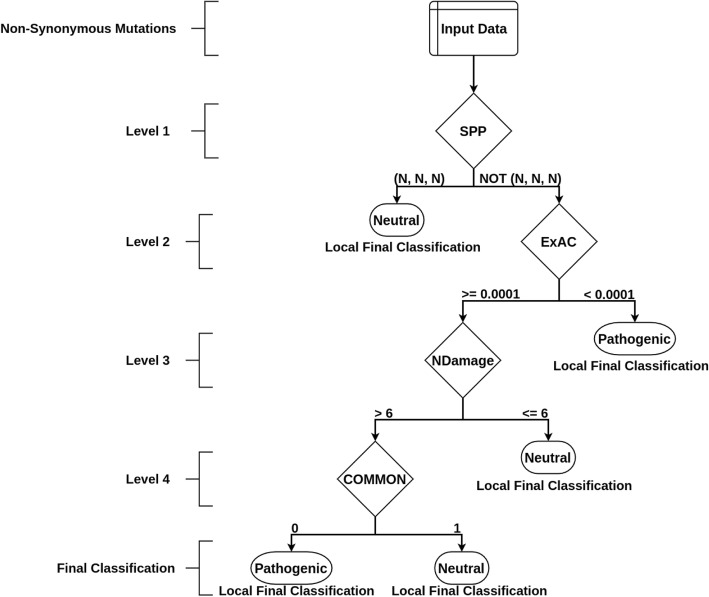
Fig. 1.
Decision tree obtained after integration and discretization of variables. Level 1: the root node, responsible for receiving input variant, separates the identified mutations in Neutral, if three predictors classify it so (in this case, variant remains not evaluated in future steps), or Pathogenic, if at least one of three predictors classify it so. Level 2: mutations classified as Pathogenic in the previous step are reevaluated according to their allele frequency in ExAC database, being reclassified as Neutral for mutations with allele frequency higher than 0.0001 (remains not evaluated in future steps), or maintained as Pathogenic, for mutations with allele frequency less than 0.0001. Level 3: Mutations previously classified as Pathogenic are reevaluated according to the number of predictors that converge to the same result. Mutations are reclassified as Neutral if identified as pathogenic by less than five predictors (remains not evaluated in future steps), or maintained as Pathogenic if identified as so by five to nine predictors. Level 4: Mutations previously classified as Pathogenic are reevaluated according to the COMMON variable from 1000genomes, being reclassified as Neutral for mutations with allele frequency higher than 0.0001, or maintained as Pathogenic, for mutations with allele frequency less than 0.0001