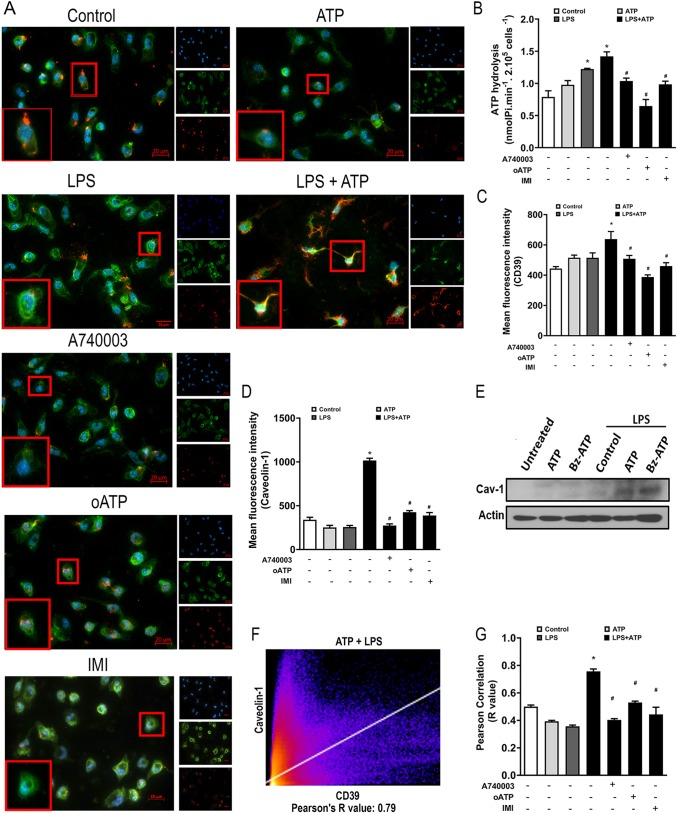
Fig. 3.
P2X7 receptor activation increases CD39 expression in caveolae of macrophages. LPS-primed peritoneal macrophages (1 µg/ml for 4 h) stimulated with 500 µM ATP for 1 h in the absence or presence of pre-treatment with the P2X7 receptor inhibitors A740003 (0.1 µM 30 min before priming), oxidized-ATP (oATP; 200 µM for 2 h before priming) or the sphingomyelinase inhibitor imipramine (IMI; 30 µM for 30 min before priming) were labeled with antibodies recognizing CD39 (green) and the lipid raft marker caveolin-1 (red), as well as with Hoechst 33258 (blue). (A) Representative immunofluorescence images of cells stained for CD39 and caveolin-1. (B-D) Enzymatic assay for ATP hydrolysis (B) and quantification of fluorescence intensity for CD39 (C) and caveolin-1 (D). (E) Representative western blot showing caveolin-1 expression in untreated and LPS-primed macrophages stimulated with P2X7 receptor agonists (500 µM ATP or 100 µM Bz-ATP). (F,G) Representative intensity histogram output (F) of Coloc2 analysis performed with Fiji/ImageJ and Pearson correlation coefficient of the pixel-intensity correlation (G) indicating colocalization. Data are expressed as mean±s.e.m. of three independent experiments. *,#P<0.05 compared with the unstimulated control or compared to the LPS+ATP group, respectively.