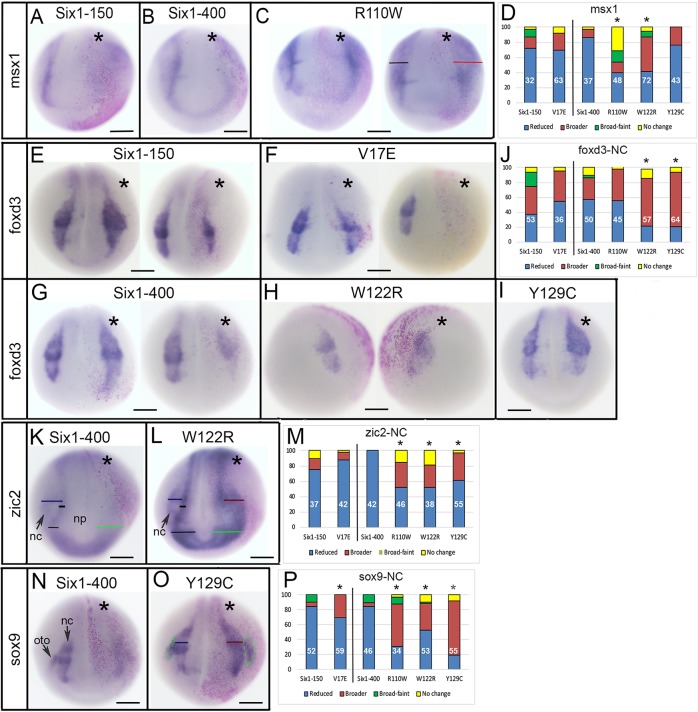
Fig. 2.
Changes in neural border and neural crest gene expression. (A,B) Both Six1WT-150 and Six1WT-400 reduce the neural border expression of msx1 on the injected side (indicated by asterisks, pink lineage tracer). (C) R110W either did not change the msx1 domain (left embryo) or caused it to be broader (right embryo, red bar) compared to the control side (black bar). (D) The expression domain size of msx1 on the Six1-mutant-injected side was compared to the control side of the same embryo and scored as reduced (blue), broader (red), broader but fainter (green) or unchanged (yellow). Phenotypes are expressed as frequencies and the sample size is within each bar (white numbers); experiments were repeated a minimum of three times. Frequencies for Six1 mutants were compared to those for embryos injected with Six1 WT mRNA; V17E was compared to Six1WT-150, and the others were compared to Six1WT-400. Significant differences between mutant and WT frequencies were assessed by the Chi-squared test (*P<0.05). (E) Six1WT-150 could either broaden (left embryo) or reduce (right embryo) the foxd3 domain. (F) V17E could either broaden (left) or reduce (right) the foxd3 domain. (G) Six1WT-400 could either broaden (left) or reduce (right) the foxd3 domain. (H,I) W122R (H) and Y129C (I) predominantly broadened the foxd3 domain. (J) Quantitation of foxd3 neural crest (NC) phenotypes, as in D. (K) Six1WT-400 broadened the anterior neural plate (np) domain (green bar) of zic2, but reduced its neural crest (nc) domain (compare to black bars and blue bar). (L) W122R caused both the anterior neural plate domain (green bar) and neural crest domain (red bar) of zic2 to broaden (compare to black and blue bars on control side). (M) Quantitation of zic2 neural crest phenotypes, as in D. (N) Six1WT-400 reduced both the neural crest and otic placode (oto) domains of sox9. (O) Y129C broadened both the neural crest (red bar) and otic placode (green dashed lines) domains of sox9. (P) Quantitation of sox9 neural crest phenotypes, as in D. Scale bars: 300 μm.