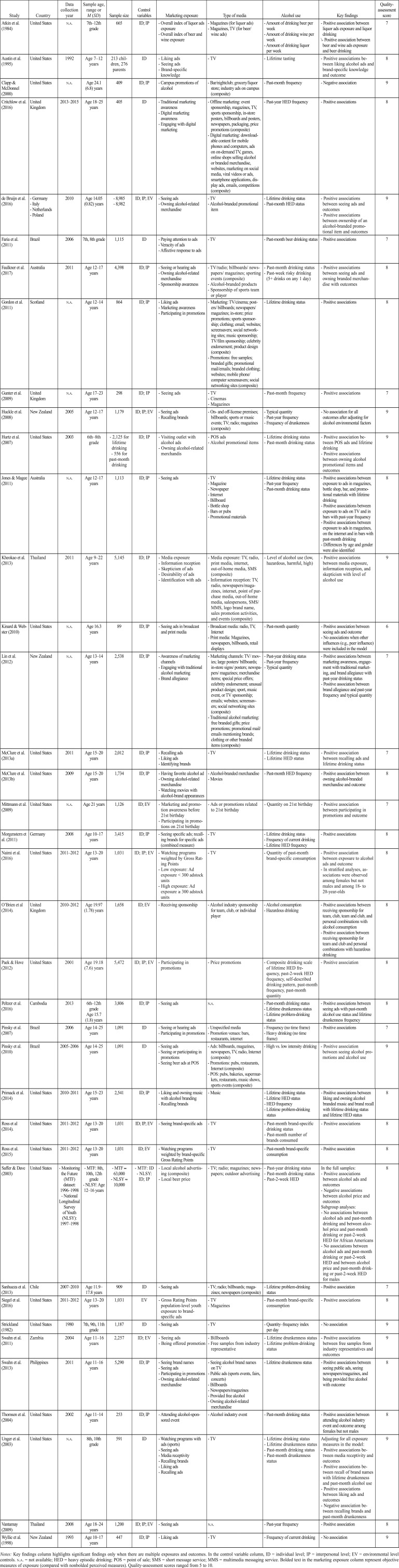
Table 1.
Summary of studies included in the systematic review
| Study | Country | Data collection year | Sample age, range or M (SD) | Sample size | Control variables | Marketing exposure | Type of media | Alcohol use | Key findings | Quality-assessment score |
| Atkin et al. (1984) | United States | n.a. | 7th–12th grade | 665 | ID; IP | - Overall index of liquor ads exposure | - Magazines (for liquor ads) | - Amount of drinking beer per week | - Positive association between liquor ads exposure and liquor drinking | 7 |
| - Overall index of beer and wine exposure | - Magazines, TV (for beer/wine ads) | - Amount of drinking wine per week | \- Positive association between beer and wine ads exposure and beer drinking | |||||||
| - Amount of drinking liquor per week | ||||||||||
| Austin et al. (1995) | United States | 1992 | Age 7–12 years | 213 children, 276 parents | ID | - Liking ads | - TV | - Lifetime tasting | - Positive associations between liking alcohol ads and brand-specific knowledge and outcome | 8 |
| - Seeing ads | ||||||||||
| - Brand-specific knowledge | ||||||||||
| Clapp & McDonnel (2000) | United States | n.a. | Age 24.1 (6.8) years | 409 | ID; IP | - Campus promotions of alcohol | - Bar/nightclub; grocery/liquor store; industry ads on campus (composite) | - Past-month frequency | - Negative association | 9 |
| Critchlow et al. (2016) | United Kingdom | 2013–2015 | Age 18–25 years | 405 | ID | - Traditional marketing awareness | - Offline marketing: event sponsorship, magazines, TV, sports sponsorship, in-store posters, billboards and posters, newspapers, packaging, price promotions (composite) | - Past-year HED frequency | - Positive associations | 8 |
| - Digital marketing awareness | - Digital marketing: downloadable content for mobile phones and computers, ads on on-demand TV, games, online shops selling alcohol or branded merchandise, websites, marketing on social media, viral videos or ads, smartphone applications, display ads, emails, competitions (composite) | |||||||||
| - Engaging with digital marketing | ||||||||||
| de Bruijn et al. (2016) | - Germany | 2010 | Age 14.05 (0.82) years | - 8,985 | ID; IP; EV | - Seeing ads | - TV | - Lifetime drinking status | - Positive associations between seeing ads and outcomes | 9 |
| - Italy | - 8,982 | - Owning alcohol-related merchandise | - Alcohol-branded promotional item | - Past-month HED status | - Positive associations between ownership of an alcohol-branded promotional item and outcomes | |||||
| - Netherlands | ||||||||||
| - Poland | ||||||||||
| Faria et al. (2011) | Brazil | 2006 | 7th, 8th grade | 1,115 | ID | - Paying attention to ads | - TV | - Past-month beer drinking status | - Positive associations | 7 |
| - Veracity of ads | ||||||||||
| - Affective response to ads | ||||||||||
| Faulkner et al. (2017) | Australia | 2011 | Age 12–17 years | 4,398 | ID; IP | - Seeing or hearing ads | - TV/radio; billboards/ newspapers/ magazines; sporting events (composite) | - Past-month drinking status | - Positive associations between seeing ads and owning branded merchandise with outcomes | 8 |
| - Owning alcohol-related merchandise | - Alcohol-branded products | - Past-week risky drinking (5+ drinks on any 1 day) | ||||||||
| - Sponsorship awareness | - Sponsorship of sports team or player | |||||||||
| Gordon et al. (2011) | Scotland | n.a. | Age 12–14 years | 864 | ID; IP | - Liking ads | - Marketing: TV/cinema; posters/billboards; newspapers/ magazines; in-store; price promotions; sports sponsorship; clothing; email; websites; screensavers; social networking sites; music sponsorship; TV/film sponsorship; celebrity endorsement; product design (composite) | - Lifetime drinking status | - Positive associations | 8 |
| - Marketing awareness | - Promotions: free samples; branded gifts; promotional mail/emails; branded clothing; websites; mobile phone/computer screensavers; social networking sites (composite) | |||||||||
| - Participating in promotions | ||||||||||
| Gunter et al. (2009) | United Kingdom | n.a. | Age 17–23 years | 298 | ID; IP | - Seeing ads | - TV | - Past-month frequency | - Positive associations | 7 |
| - Cinemas | ||||||||||
| - Magazines | ||||||||||
| Huckle et al. (2008) | New Zealand | 2005 | Age 12–17 years | 1,179 | ID; IP; EV | - Seeing ads | - On- and off-license premises; billboards; sports or music events; TV; radio; magazines (composite) | - Typical quantity | - No association for all outcomes after adjusting for alcohol environmental factors | 9 |
| - Recalling brands | - Past-year frequency | |||||||||
| - Frequency of drunkenness | ||||||||||
| Hurtz et al. (2007) | United States | 2003 | 6th–8th grade | - 2,125 for lifetime drinking | ID; IP | - Visiting outlet with alcohol ads | - POS ads | - Lifetime drinking status | - Positive association between POS ads and lifetime drinking | 9 |
| - 556 for past-month drinking | - Owning alcohol-related merchandis | - Alcohol promotional items | - Past-month drinking status | - Positive associations between owning alcohol promotional items and outcomes | ||||||
| Jones & Magee (2011) | Australia | n.a. | Age 12–17 years | 1,113 | ID; IP | - Seeing ads | - TV | - Lifetime drinking status | - Positive associations between exposure to ads in magazines, bottle shop, bar, and promotional materials with lifetime drinking | 8 |
| - Magazine | - Past-year frequency | - Positive associations between exposure to ads on TV and in bars with past-year frequency | ||||||||
| - Newspaper | - Past-month drinking status | - Positive associations between exposure to ads in magazines, on the internet and in bars with past-month drinking | ||||||||
| - Internet | - Differences by age and gender were also identified | |||||||||
| - Billboard | ||||||||||
| - Bottle shop | ||||||||||
| - Bars or pubs | ||||||||||
| - Promotional materials | ||||||||||
| Kheokao et al. (2013) | Thailand | 2011 | Age 9–22 years | 5,145 | ID; IP | - Media exposure | - Media exposure: TV, radio, print media, internet, out-of-home media, SMS (composite) | - Level of alcohol use (low, hazardous, harmful, high) | - Positive associations between media exposure, information reception, and skepticism with level of alcohol use | 9 |
| - Information reception | - Information reception: TV, radio, newspapers/magazines, internet, point of purchase media, out-of-home media, salespersons, SMS/MMS, logo brand name, sales promotion activities, and events (composite) | |||||||||
| - Skepticism of ads | ||||||||||
| - Desirability of ads | ||||||||||
| - Identification with ads | ||||||||||
| Kinard & Webster (2010) | United States | n.a. | Age 16.3 years | 89 | ID; IP | - Seeing ads in broadcast and print media | - Broadcast media: radio, TV, Internet | - Past-month quantity | - Positive association between seeing ads and outcome | 6 |
| - Print media: Magazines, newspapers, billboards, retail displays | - No associations when other influences (e.g., peer influence) were included in the model | |||||||||
| Lin et al. (2012) | New Zealand | n.a. | Age 13–14 years | 2,538 | ID; IP | - Awareness of marketing channels | - Marketing channels: TV/ movies; large posters/ billboards; in-store signs/ posters; newspapers/ magazines; merchandise items; special price offers; celebrity endorsement; unusual product design; sport, music event, or TV sponsorship; emails; websites; screensavers; social networking sites (composite) | - Past-year drinking status | - Positive associations between marketing awareness, engagement with traditional marketing, and brand allegiance with past-year drinking status | 7 |
| - Engaging with traditional alcohol marketing | - Traditional alcohol marketing: free branded gifts; price promotions; promotional mail/emails mentioning brands; clothing or other branded items (composite) | - Past-year frequency | - Positive association between brand allegiance and past-year frequency and typical quantity | |||||||
| - Brand allegiance | - Typical quantity | |||||||||
| McClure et al. (2013a) | United States | 2011 | Age 15–20 years | 2,012 | ID; IP | - Recalling ads | - TV | - Lifetime drinking status | - Positive association between recalling ads and lifetime drinking status | 7 |
| - Liking ads | - Lifetime HED status | |||||||||
| - Identifying brands | ||||||||||
| McClure et al. (2013b) | United States | 2009 | Age 15–20 years | 1,734 | ID; IP | - Having favorite alcohol ad | - Alcohol-branded merchandise | - Past-month HED frequency | - Positive association between owning alcohol-branded merchandise and outcome | 8 |
| - Owning alcohol-related merchandise | - Movies | |||||||||
| - Watching movies with alcohol-brand appearances | ||||||||||
| Mittmann et al. (2009) | United States | n.a. | Age 21 years | 1,126 | ID; EV | - Marketing and promotion awareness before 21st birthday | - Ads or promotions related to 21st birthday | - Quantity on 21st birthday | - Positive association between participating in promotions and outcome | 7 |
| - Participating in promotions on 21st birthday | ||||||||||
| Morgenstern et al. (2011) | Germany | 2008 | Age 10–17 years | 3,415 | ID; IP | - Seeing specific ads; recalling brands for specific ads (combined measure) | - TV | - Lifetime drinking status | - Positive associations | 8 |
| - Frequency of current drinking | ||||||||||
| - Lifetime HED frequency | ||||||||||
| Naimi et al. (2016) | United States | 2011–2012 | Age 13–20 years | 1,031 | ID; IP; EV | - Watching programs weighted by Gross Rating Points | - TV | - Quantity of past-month brand-specific consumption | - Positive association between exposure to alcohol ads and outcome | 8 |
| - Low exposure: Ad exposure < 300 adstock units | - In stratified analyses, associations were observed among females but not males and among 18- to 20-year-olds | |||||||||
| - High exposure: Ad exposure ≥ 300 adstock units | ||||||||||
| O’Brien et al (2014). | United Kingdom | 2010–2012 | Age 19.97 (1.78) years | 1,658 | ID; EV | - Receiving sponsorship | - Alcohol industry sponsorship for team, club, or individual player | - Alcohol consumption | - Positive associations between receiving sponsorship for team, club, team and club, and personal combinations with alcohol consumption | 8 |
| - Hazardous drinking | - Positive association between receiving sponsorship for team and club and personal combinations with hazardous drinking | |||||||||
| Paek & Hove (2012) | United States | 2001 | Age 19.18 (7.6) years | 5,472 | ID; IP; EV | - Participating in promotions | - Price promotions | - Composite drinking scale of lifetime HED frequency, past-2-week HED frequency, self-described drinking pattern, past-month frequency, past-month quantity | - Positive association | 8 |
| Peltzer et al. (2016) | Cambodia | 2013 | 6th–12th grade Age 15.7 (1.8) years | 3,806 | ID; IP | - Seeing ads | n.a. | - Past-month drinking status | - Positive associations between seeing ads with past-month alcohol use status and lifetime drunkenness frequency | 8 |
| - Lifetime drunkenness status | ||||||||||
| - Lifetime problem-drinking status | ||||||||||
| Pinsky et al. (2007) | Brazil | 2006 | Age 14–25 years | 1,091 | ID | - Seeing or hearing ads | - Unspecified media | - Frequency (no time frame) | - Positive associations | 7 |
| - Participating in promotions | - Promotion venues: bars, restaurants, internet | - Heavy drinking (no time frame) | ||||||||
| Pinsky et al. (2010) | Brazil | 2005–2006 | Age 14–25 years | 1,091 | ID | - Seeing ads | - Ads: billboards, magazines, newspapers, TV, radio, Internet (composite) | - High vs. low intensity drinking | - Positive association between seeing alcohol promotions and alcohol use | 9 |
| - Seeing or participating in promotions | - Promotions: pubs, restaurants, Internet (composite) | |||||||||
| - Seeing beer ads at POS | - POS: pubs, bakeries, supermarkets, restaurants, music shows, sports events (composite) | |||||||||
| Primack et al. (2014) | United States | 2010–2011 | Age 15–23 years | 2,541 | ID; IP | - Liking and owning music with alcohol branding | - Music | - Lifetime drinking status | - Positive associations between liking and owning alcohol branded music and brand recall with lifetime drinking status and lifetime HED status | 8 |
| - Recalling brands | - Lifetime HED status | |||||||||
| - HED frequency | ||||||||||
| - Lifetime problem-drinking status | ||||||||||
| Ross et al (2014). | United States | 2011–2012 | Age 13–20 years | 1,031 | ID; IP; EV | - Seeing brand-specific ads | - TV | - Past-month brand-specific drinking status | - Positive associations | 8 |
| - Past-month number of brands consumed | ||||||||||
| Ross et al (2014). | United States | 2011–2012 | Age 13–20 years | 1,031 | ID; EV | - Watching programs weighted by brand-specific Gross Rating Points | - TV | - Past-month brand-specific consumption | - Positive associations | 8 |
| Saffer & Dave (2003) | United States | - Monitoring the Future (MTF) dataset: 1996–1998 | - MTF: 8th, 10th, 12th grade | - MTF ≈ 63,000 | - MTF: ID | - Local alcohol advertising (composite) | - TV; radio; magazines; newspapers; outdoor advertising | - Past-year drinking status | In the full samples: | 8 |
| - National Longitudinal Survey of Youth (NLSY): 1997–1998 | - NLSY: Age 12–16 years | - NLSY ≈ 10,000 | - NLSY: ID; IP | - Local beer price | - Past-month drinking status | - Positive associations between alcohol ads and outcomes | ||||
| - Past-2-week HED | - Negative associations between alcohol price and outcomes | |||||||||
| Subgroup analyses: | ||||||||||
| - No associations between alcohol ads and past-month drinking and between alcohol price and past-month drinking or past-2-week HED for African Americans | ||||||||||
| - No associations between alcohol ads and past-month drinking or past-2-week HED and between alcohol price and past-month drinking or past-2-week HED for males | ||||||||||
| Sanhueza et al. (2013) | Chile | 2007–2010 | Age 11.9–17.8 years | 909 | ID | - Seeing ads | - TV; radio; billboards; magazines; newspapers (composite) | - Lifetime problem-drinking status | - Positive association | 7 |
| Siegel et al. (2016) | United States | 2011–2012 | Age 13–20 years | 1,031 | EV | - Gross Rating Points population-level youth exposure to brandspecific ads | - TV | - Past-month brand-specific consumption | - Positive associations | 8 |
| - Magazines | ||||||||||
| Strickland (1982) | United States | 1980 | 7th, 9th, 11th grade | 1,187 | ID | - Seeing ads | - TV | - Quantity–frequency index per day | - No association | 9 |
| Swahn et al. (2011) | Zambia | 2004 | Age 11–16 years | 2,257 | ID; EV | - Seeing ads | - Billboards | - Lifetime drunkenness status | - Positive associations between free samples from industry representatives and outcomes | 9 |
| - Being offered promotion | - Free samples from industry representative | - Lifetime problem-drinking status | ||||||||
| Swahn et al. (2013) | Philippines | 2011 | Age 11–16 years | 5,290 | ID; IP | - Seeing brand names | - Seeing alcohol brand names on TV | - Lifetime drunkenness status | - Positive associations between seeing public ads, seeing newspapers/magazines, and being provided free alcohol with outcome | 8 |
| - Seeing ads | - Public ads (sports events, fairs, concerts) | |||||||||
| - Participating in promotions | - Billboards | |||||||||
| - Owning alcohol-related merchandise | - Newspapers/magazines | |||||||||
| - Provided free alcohol | ||||||||||
| - Owning alcohol-related merchandise | ||||||||||
| Thomsen et al. (2004) | United States | 2002 | Age 11–14 years | 253 | ID; IP | - Attending alcohol-sponsored event | - Alcohol industry event | - Past-month drinking status | - Positive association between attending alcohol industry event and outcome among females but not males | 8 |
| Unger et al. (2003) | United States | n.a. | 8th, 10th grade | 591 | ID | - Watching programs with ads (sports) | - TV | - Lifetime drinking status | Adjusting for all exposure measures in the model: | 9 |
| - Seeing ads | - Lifetime drunkenness status | - Positive associations between media receptivity and outcomes | ||||||||
| - Media receptivity | - Past-month drinking status | - Positive associations between recall of brand names with lifetime drunkenness and past-month alcohol use | ||||||||
| - Recalling brands | - Past-month drunkenness status | - Positive associations between liking ads and outcomes | ||||||||
| - Negative association between recalling brands and past-month drunkenness | ||||||||||
| - Liking ads | ||||||||||
| - Recalling ads | ||||||||||
| Vantamay (2009) | Thailand | 2008 | Age 18–24 years | 1,200 | ID; IP; EV | - Seeing ads | n.a. | - Past-year frequency | - Positive association | 8 |
| Wyllie et al. (1998) | New Zealand | 1993 | Age 10–17 years | 447 | ID; IP | - Liking ads | - TV | - Frequency of current drinking | - No association | 9 |
Notes: Key findings column highlights significant findings only when there are multiple exposures and outcomes. In the control variable column, ID = individual level; IP = interpersonal level; EV = environmental level controls. n.a. = not available; HED = heavy episodic drinking; POS = point of sale; SMS = short message service; MMS = multimedia messaging service. Bolded text in the marketing exposure column represent objective measures of exposure (compared with nonbolded perceived measures). Quality-assessment scores ranged from 5 to 10.