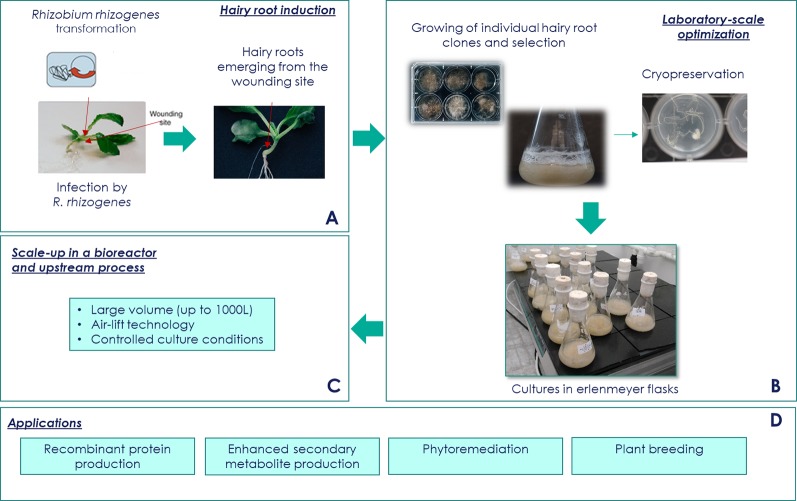
Figure 2.
Hairy root culture platform. (A) Hairy root culture (HRC) induction. The efficiency of transformation depends on different factors such as type of explant and age, and the strain and density of Rhizobium rhizogenes. Acetosyringone addition can help to permeate the cell walls and plant membranes promoting better infection efficiency. After infection, the use ofantibiotics to eliminate excess of bacteria is necessary. (B) Conservation and pre-bioreactor stage. Storage clones in master/working transgenic bank is possible using cryoconservation method. In another way, several strategies can be used to improve the yields of the desired compounds. Among these strategies, there is inoculum and nutrient medium optimization, elicitation, selection of high-producing lines, metabolic engineering approaches, permeabilization, and two-phase systems cultivation. (C) Bioreactor stage. Different conditions can be optimized according to the desired outcome. Some of the optimizable variables are bioreactor operation mode (batch, fed-batch), culture conditions (air flow rate, temperature), hardware configurations (drive wave reactor, pneumatically driven bubble column bioreactor, and gas-phase bed reactor also referred to as “mist bioreactor”). Another medium-scale up culture approach is the use of shaken flasks using orbital shaker with HRC grown in liquid medium. (D) Applications. Among the possible molecules derived from HRCs there are specialized metabolites and recombinant proteins. Transgenic HRs can also be used for phytoremediation or mechanism understanding.