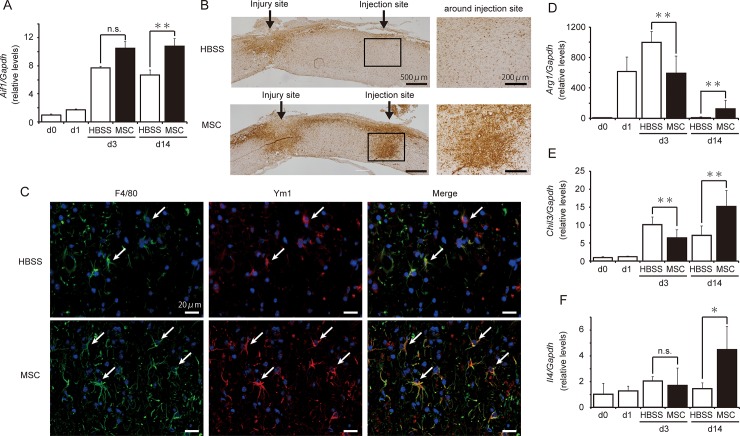
Fig 7. Human mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (hMSCs) increased levels of alternatively activated macrophages (AAM) and anti-inflammatory cytokines.
(A) The transplantation of hMSCs significantly increased the levels of Aif1 expression on postoperative day (pod) 14 (n = 9 mouse) relative to those observed in the HBSS-treated animals (n = 8 mouse). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. **: P < 0.01 (Dunnett’s post hoc test), n.s.: not significant. (B) Iba1-positive MG/MΦ were clustered around the site of hMSC injection on pod 14 (n = 3 mouse in each group). (C) F4/80+ cells (green) exhibited greater overlap with Ym1+ cells (red) around the injection site in the hMSC-treated group than in the HBSS-treated group. Nuclear staining was performed using DAPI. Transplantation of hMSCs significantly increased the expression of the AAM markers Arg1 (D) and Chil3 (E), as well as that of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-4 (F) on pod 14. All data are expressed the relative level (fold) to compare with pod 0 (basal level, n = 6 mouse) after normalization against Gapdh as a housekeeping gene. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. *: P<0.05, **: P < 0.01 (Dunnett’s post hoc test), n.s.: not significant.