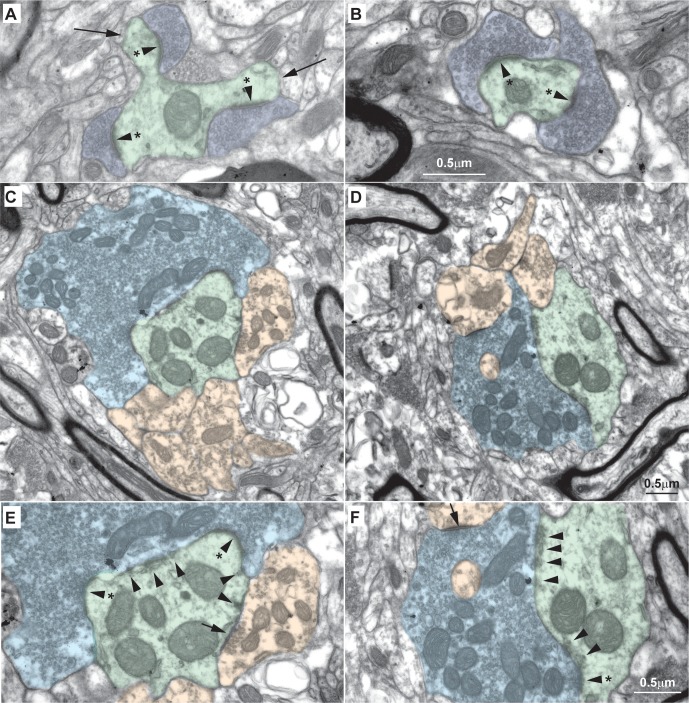
Fig 8. Fine structure of excitatory profiles in the MDmc of the macaque thalamus.
(A, B) Some axon terminals in the MDmc are small, contain round vesicles, and form asymmetric (excitatory) synapses (arrowheads with asterisk, A and B). These round vesicle, small terminals (RSs; dark blue, A and B) form synapses with typical dendrites, some of which have cytoplasmic expansions (thorns, long arrows, A), that likely are part of thalamic relay neurons; we refer to these dendrites as EDs (green, A and F). (C–F) Other axon terminals in the MDmc are large, contain round vesicles, and form asymmetric (excitatory) synapses (arrowheads with asterisk, E and F). These large terminals with round vesicles, known as RLs (light blue, C–F) form synapses with EDs (green, C–F). RLs also form synapses with dendrites that have flat and pleomorphic vesicles and form symmetric (inhibitory) synapses (short arrow, E) with EDs. Dendrites with flat and pleomorphic vesicles are inhibitory (IDs; orange in C–F). RL terminals that form synapses with EDs also show many nonsynaptic contacts called puncta adherentia (arrowheads, E and F), a nonsynaptic adhesion; IDs also form some puncta adherentia with EDs (E). Calibration bar in B applies to A, B. Calibration bar in D applies to C, D. Calibration bar in F applies to E, F. ED, excitatory dendrite; ID, inhibitory dendrite; MDmc, mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, magnocellular part; RL, round vesicles, large terminal; RS, round vesicles, small terminal.