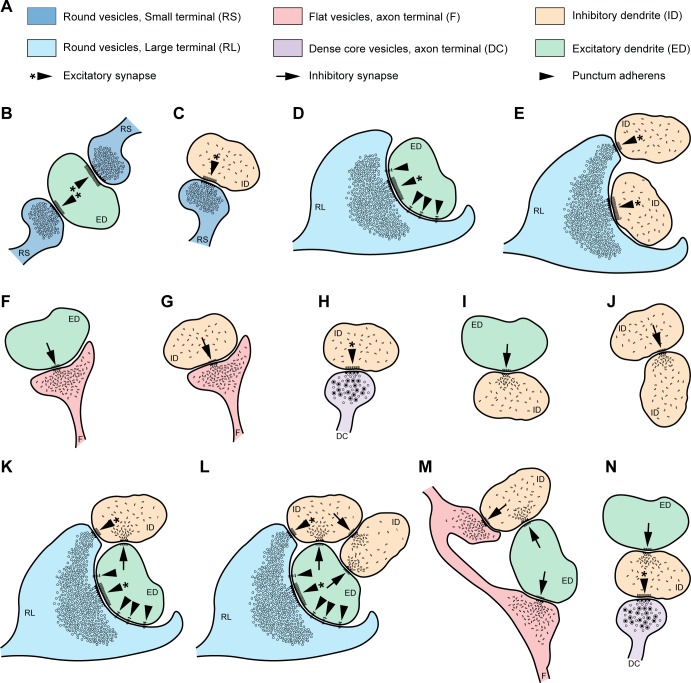
Fig 10. Summary of synaptic interactions in the MDmc of the rhesus macaque.
(A) Summary of pre- and postsynaptic profiles and types of synaptic and nonsynaptic contacts between neurons found in the MDmc; color codes and abbreviations used are the same as in Figs 8 and 9. (B) RSs form excitatory synapses with EDs. (C) RSs also form excitatory synapses with IDs. (D) RLs form excitatory synapses and show several puncta adherentia (nonsynaptic structures) with EDs. (E) RLs also form excitatory synapses with IDs. (F, G) F terminals form inhibitory synapses with EDs (F) and IDs (G). (H) A terminal with DCs, which is likely catecholaminergic, forms an excitatory synapse with an ID. (I) An ID forms an inhibitory synapse with an ED. (J) An ID forms an inhibitory synapse with an ID. (K) The classical triadic arrangement consists of one RL that forms an excitatory synapse with one relay ED and another synapse on one ID; the same ID forms a synapse with the relay ED. (L) More complex synaptic arrangements consist of a classical triad (as in K) and one ID that inhibits both the ID and ED of the triad. (M) In inhibitory triads, described here for the first time, to our knowledge, 2 axon terminals of F type along the same axon form a synapse with one ED and another synapse on an ID; the same ID forms a synapse with the relay ED. (N) The axon terminal with DCs that we identified formed an excitatory synapse with one ID, which in turn formed an inhibitory synapse on one ED. DC, dense-core vesicle; ED, excitatory dendrite; F, inhibitory axon terminal; ID, inhibitory dendrite; MDmc, mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, magnocellular part; RL, round vesicles, large terminal; RS, round vesicles, small terminal.