Fig. 9.
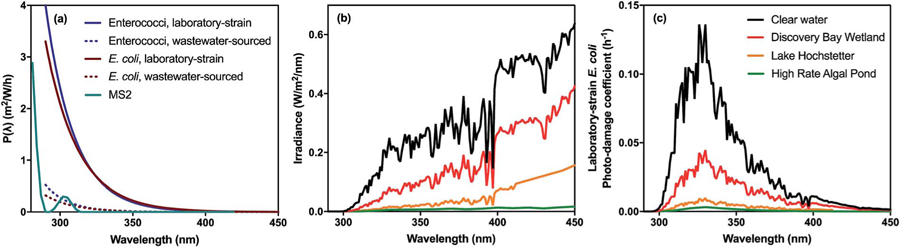
Impact of action spectrum and sunlight attenuation in the water column on the endogenous inactivation rate constant for diverse waters. The action spectra for different microorganisms are shown in panel (a). In panel (b) the irradiance spectrum averaged over 20 cm depth is shown for different waters (a subset of those in Fig. 3). In panel (c) we show the photodamage coefficient for lab-strain E. coli, which is the product of the action spectrum and the irradiance spectrum averaged over a 20 cm depth. The area under the photodamage spectrum is kendo. Irradiance spectra were determined for a single atmospheric condition (as reported in Silverman et al.,17 for a summer day at 38° latitude), accounting for attenuation in the water column for the waters shown in Fig. 3. Resulting values for kendo for the different waters are: clear water (5.2 h−1), Discovery Bay Wetland (1.9 h−1), Lake Hochstetter (0.41 h−1), and High Rate Algal Pond (0.12 h−1). Biological weighting functions for bacteria are from Silverman et al. (2016) and for MS2 was modified from Fisher et al. (2011).111,151
