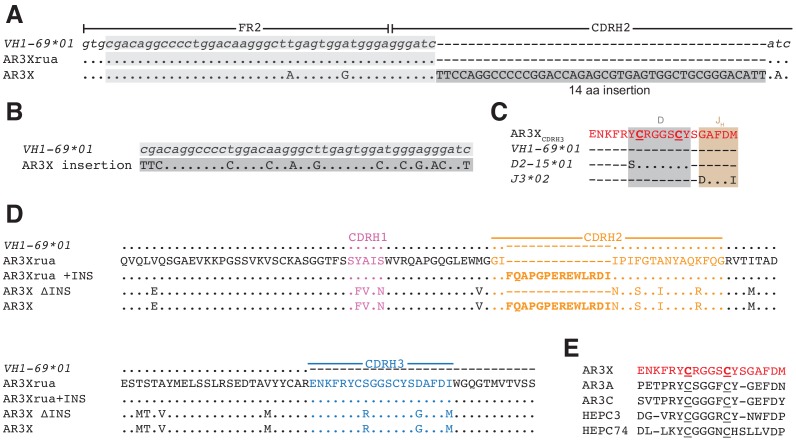
Figure 1. AR3X includes a 14-residue insertion in CDRH2.
(a) Sequence alignment of a portion of the heavy chain variable region gene sequences of AR3X and the AR3X germline precursor (AR3Xrua) (uppercase letters) and the VH1-69 gene segment (lowercase letters). The CDRH2 insertion is indicated by a dark gray box with the position of the potential duplication site indicated by a light gray box. CDR loops were defined based on Kabat nomenclature Kabat and National Institutes of Health (U.S.). Office of the Director, 1991). Dots indicate identical nucleotides and dashes indicate gaps. (b) Sequence alignment of the CDRH2 insertion and the potential duplication origin site in VH1-69. (c) Amino acid sequence alignment of the AR3X CDRH3 and the AR3X germline precursor genes determined by IMGT/V-QUEST. Dots indicate identical amino acids and dashes indicate regions encoded by other gene segments or N-nucleotide additions. Two cysteines encoded by the D gene segment are highlighted in bold and underscored. (d) Amino acid sequence alignment of the heavy chain variable region sequences of AR3X, AR3X ΔINS (AR3X without insertion), AR3Xrua (germline precursor of AR3X), and AR3Xrua + INS (germline precursor of AR3X with insertion). CDR loops were defined based on Kabat nomenclature and colored purple (CDRH1), orange (CDRH2), and blue (CDRH3), with the CDRH2 insertion highlighted in bold. Dots indicate identical amino acids and dashes indicate gaps. (e) Alignment of AR3X, AR3A, AR3C, HEPC3, and HEPC74 CDRH3 sequences. The AR3X sequence is highlighted in red and the two cysteines in each CDRH3 are underscored.