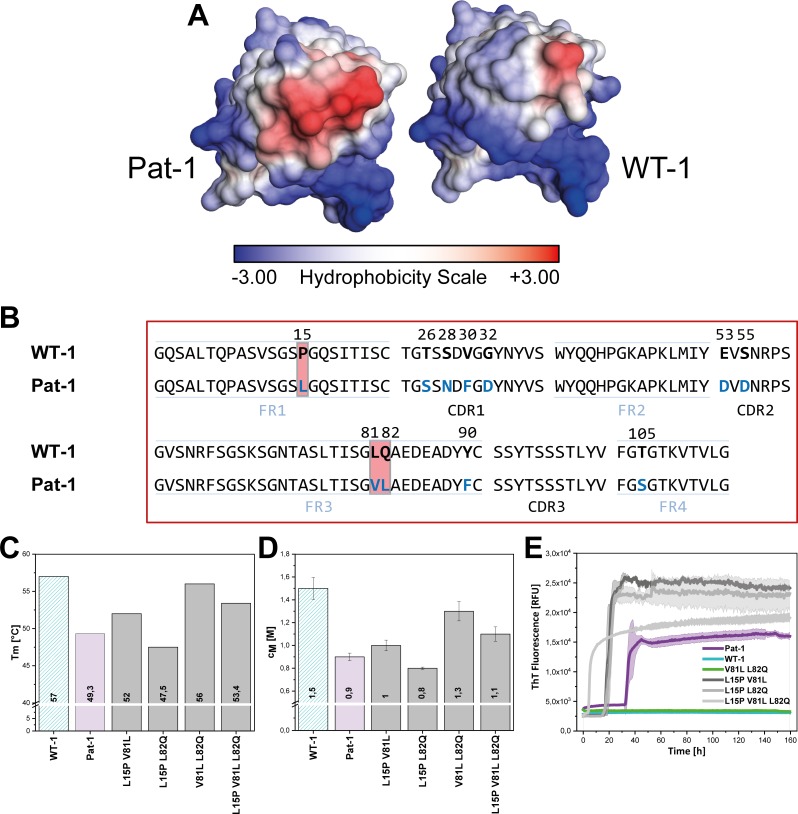
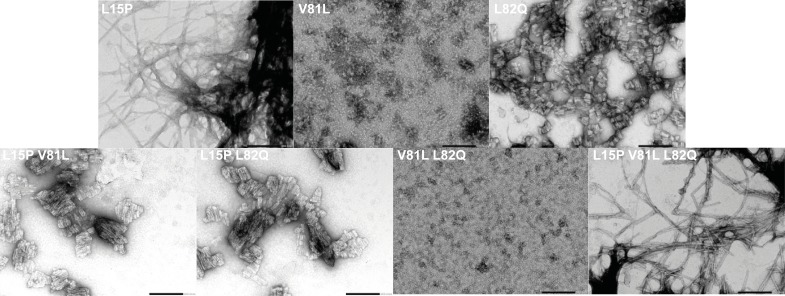
Figure 4. Influence of amino acid substitutions altering the hydrophobic of Pat-1.
(A) Surface representation of the crystal structures of Pat-1 and WT-1. The surface amino acids are colored according to their hydrophobicity. (B) Sequences of Pat-1 and WT-1 with the amino acids located in the hydrophobic surface patch of the VL domains highlighted in red. (C) Thermal and (D) chemical stabilities of WT-1, Pat-1 and the single, double and triple point mutants varying the hydrophobic surface of Pat-1. Thermal stabilities were obtained by fitting the thermal unfolding data to a Boltzmann fit. Chemical stabilities were obtained by fitting GdmCl unfolding data according to a two-state unfolding model. The measurement was performed three times and the mean was taken. (E) Fibril formation was followed by ThT fluorescence. The assay was performed in PBS buffer containing 0.5 mM SDS at 37°C and shaking. The continuous lines show the mean value of triplicates with SD as transparent colored areas.