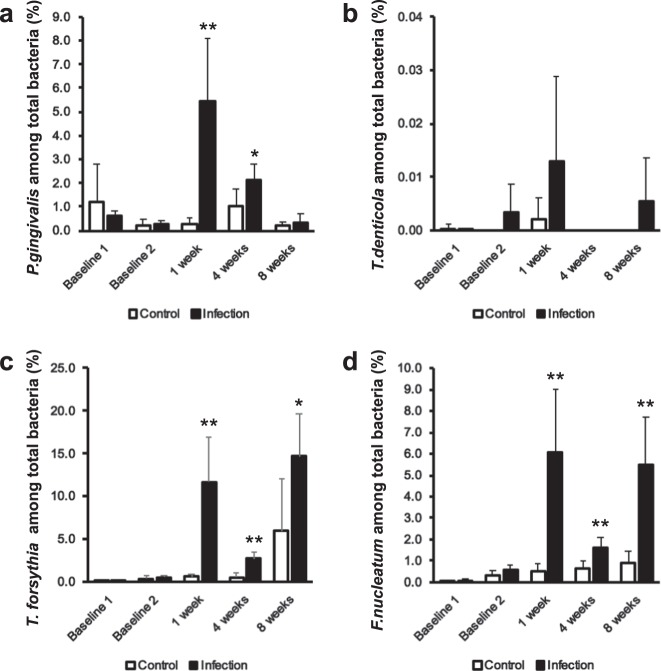
Fig. 2. A polymicrobial oral infection can be successfully obtained in a common mouse strain.
Oral swab samples were collected from the teeth, oral mucosa, and gingiva of mice with micro cotton tip swabs to evaluate microbial status of the polymicrobial infection model. DNA was isolated and purified from the swab samples, which were collected at different time points (baseline 1; before infection and before an antibiotic wash out; baseline 2; before infection and after an antibiotic washout, and 1, 4, and 8 weeks after infection) and then the four periodontal pathogens (P. gingivalis, T. denticola, T. forsythia, and F. nucleatum) and total bacteria were quantified by standard real-time PCR using primers corresponding to 16S ribosomal RNA. a–d The data are shown as a percentage of each pathogen among total bacteria; mean ± s.d.