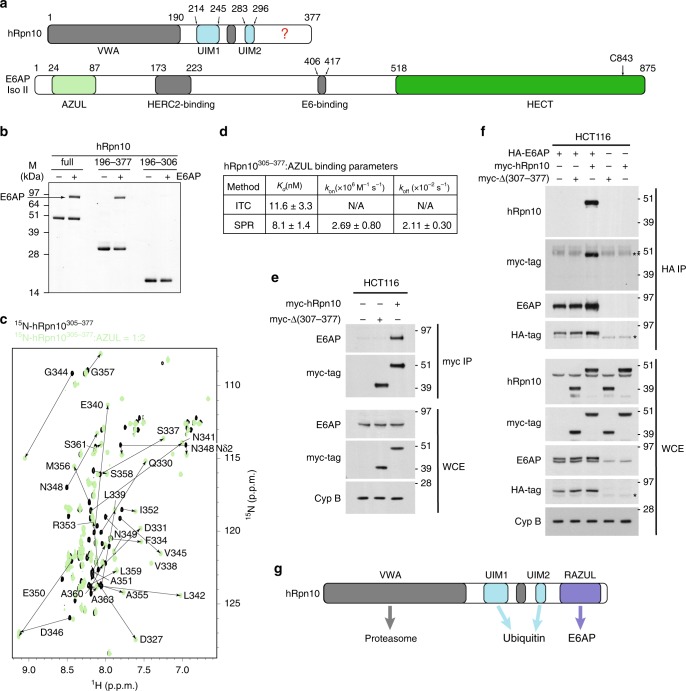
Fig. 1. A C-terminal domain in hRpn10 binds E6AP AZUL.
a Positions of known functional domains within hRpn10 (top) and E6AP isoform II (bottom). Question mark “?” indicates hRpn10 uncharacterized region and the E6AP catalytic cysteine C843 is indicated. b Pull-down assay of His-tagged hRpn10full-length (full), hRpn10196–377 or hRpn10196–306 without (−) or with (+) incubation of E6AP. c 1H, 15N HSQC spectra of 0.2 mM 15N-hRpn10305–377 (black) and with twofold molar excess unlabeled AZUL (green). Shifted signals are labeled. d Table summarizing Kd, kon, and koff average values with standard deviations for the hRpn10305–377: AZUL interaction measured by ITC and/or SPR. N/A, not applicable. e HCT116 lysates expressing empty vector, myc-hRpn10 full length, or myc-Rpn10 with RAZUL deleted (Δ307–377) were subjected to myc-immunoprecipitation with anti-myc-tag nanobody-coupled agarose. Whole cell extracts (WCE) and myc-immunoprecipitates were immunoprobed with the indicated antibodies. Cyclophilin B (Cyp B) is used as a loading control in e and f. f Lysates from HCT116 cells expressing HA-E6AP and the myc-hRpn10 constructs of e were subjected to HA IP followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. An asterisk “*” indicates non-specific interaction; double asterisk “**” indicates heavy chain antibody. e–f All antibodies used for immunoprobing are indicated to the left of the images. Note that the hRpn10 and E6AP antibodies recognize both endogenous and exogenously expressed protein, causing these panels to show both tagged and endogenous protein. g Schematic representation highlighting interaction domains of hRpn10 including newly identified RAZUL. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.