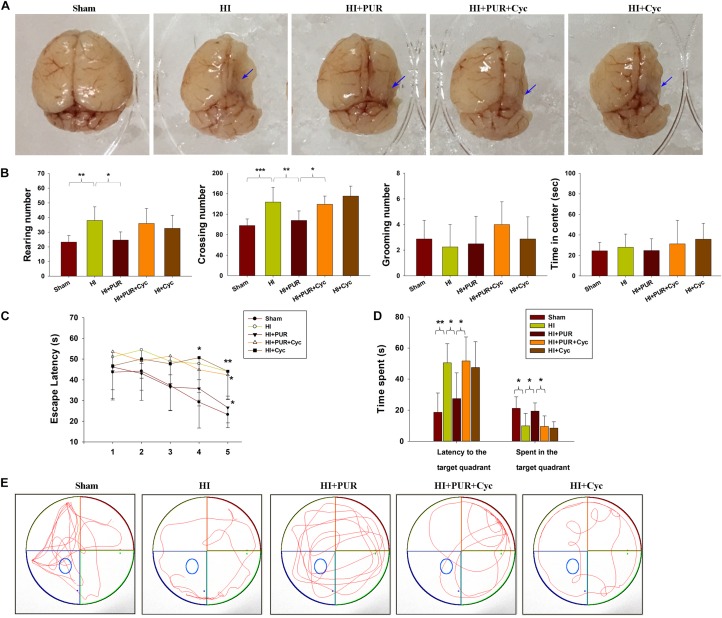
FIGURE 8.
Effects of PUR on brain atrophy and behavioral changes following HI insult. (A) Representative morphology of the brain of each group at 14 days post-HI. Arrows indicate atrophy within the ipsilateral hemisphere. (B) Locomotion was measured within an open field test (N = 8/group). Each mouse was placed in the corner of the box and allowed 5 min of exploration. The following behaviors were recorded for each mouse: number of squares crossed (crossing), frequency of standing on hind limbs (rearing), number of times the animal was observed grooming their face, licking/cleaning and scratching various parts of the body (grooming), and amount of time traveled in the center area of the maze. (C) During each acquisition trial in the MWM test, all the animals were allowed 60 s per trial to locate the escape platform, which was submerged 2 cm below the water surface and located in the center of quadrant III. The time required to locate and climb onto the platform (escape latency) was measured for 5 consecutive days (four trials/day). (D) On probe trial (day 6), the platform was removed from the tank. Animals were placed in quadrant IV and their swimming path was traced for the following 60 s of the test. The time to reach the original platform in the target zone and total time traveled in the target zone were recorded. (E) Display of tracks of all groups on day 6 (N = 8/group). Values represent the mean ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 daily scores were compared using ANOVA with Bonferroni correction.