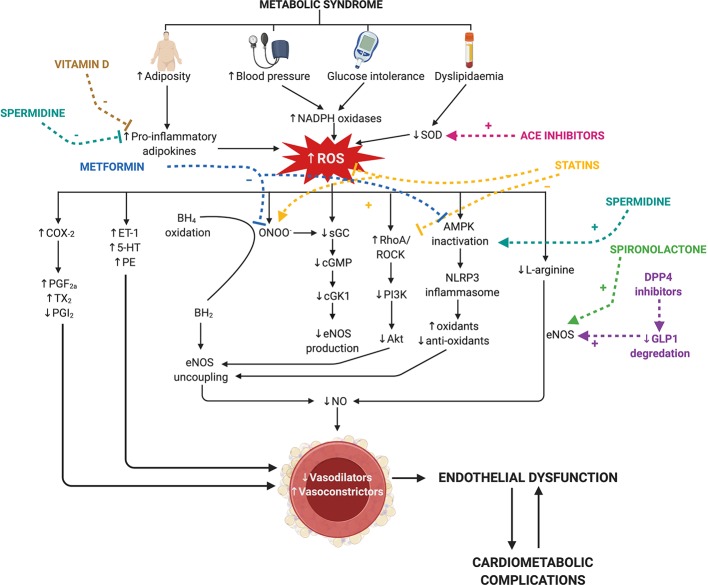
Figure 1.
Current therapies for the comorbidities of metabolic syndrome, targetting nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species signaling in endothelial dysfunction. Metabolic syndrome is characterized by an increase in visceral adiposity, blood pressure, glucose intolerance, and dyslipidemia. Individually, these co-morbidities induce endothelial dysfunction by increasing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reducing nitric oxide (NO; pathways indicated in black). ROS is increased via increases in nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase and pro-inflammatory adipokines and reductions in superoxide dismutase (SOD). This reduces endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) production via two key mechanisms: reduced L-arginine conversion and soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) activity. Uncoupling of eNOS occurs via two mechanisms [tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) and 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) inactivation] to further reduce eNOS activity. Increased cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) activity drives the production of vasoconstrictor prostanoids (PGF2a, prostaglandin F2α; TXA2, thromboxane A2) and decreases prostacyclin (PGI2) production. ROS also drives the production of other endothelium-derived contracting factors (ET-1= endothelin-1, 5-HT= serotonin and PE= phenylephrine). Many first-line therapeutic drugs for the co-morbidities of metabolic syndrome (colored) target these mechanisms. Metformin (blue) reduces AMPK inactivation and peroxynitrite (ONOO-) production. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (pink) reduce SOD activity. Statins (yellow) reduce AMPK inactivation and ROS production and increase sGC activity. Spironolactone and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) increase eNOS activity. Spermidine (turquoise) and vitamin D (dark yellow) inhibit the activation of pro-inflammatory adipokines released from adipose tissue, and spermidine promotes AMPK activation. BH2, 7,8-dihydrobiopterin; cGMP, cyclic guanosine-3′,5′-monophosphate; cGK1, cGMP-dependent protein kinase-1; ROCK, RhoA associated protein kinase; GLP1, glucagon-like peptide 1. Created with BioRender.com.