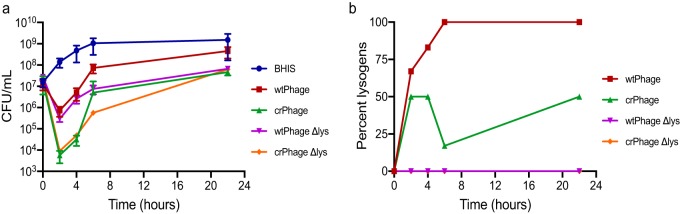
FIG 2.
In vitro comparison of the activity and lysogen formation rates of wild-type and engineered phage variants. (a) Time course of the reduction in the numbers of CFU during in vitro infection by bacteriophage at an input MOI of 0.1. CRISPR-engineered phage offers a clear improvement in the reduction in the numbers of CFU between 2 and 6 h, but by 24 h, all phage-treated cultures recover. Interestingly, there was no observable effect of lysogeny gene knockout on the activity of the phage. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. BHIS, brain heart infusion supplemented with 0.1% taurocholate. (b) Time course of PCR-based detection of lysogeny in surviving bacterial colonies after phage infection. The CRISPR-enhanced phage exhibits impaired lysogen formation. Phage variants lacking key lysogeny genes exhibit no detectable lysogeny in vitro. Two biological replicates were performed per treatment per experiment.