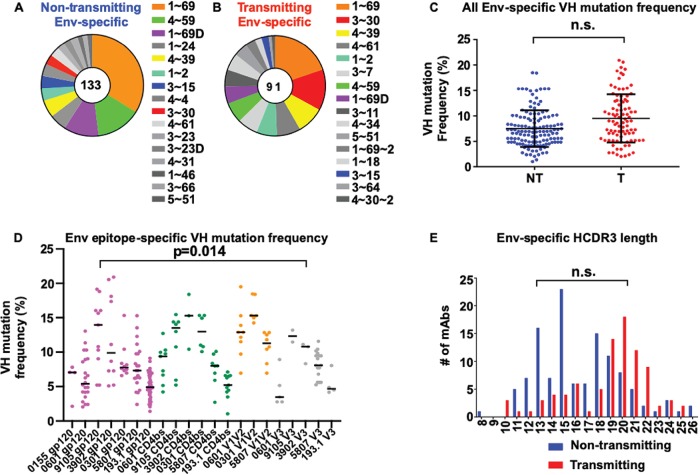
FIG 1.
Immunogenetic characteristics of Env-specific IgG MAbs isolated from HIV-infected U.S. and Malawian women. (A and B) VH gene usage of Env-specific IgG MAbs isolated from nontransmitting and transmitting women. (C) VH somatic hypermutation frequency of HIV Env-specific IgG MAbs isolated from nontransmitting (blue) (NT) and transmitting (red) (T) women. n.s., differences were not statistically significant. (D) VH somatic hypermutation frequency of gp120, V1V2, V3, and CD4 binding site-specific IgG MAbs. VH somatic hypermutation frequencies were statistically significantly different across different epitope specificities (ANOVA P = 0.014). (E) HCDR3 amino acid length of Env-specific IgG MAbs. The P value in panel D compares the VH somatic hypermutation frequency of V1V2 to those of V3, the CD4 binding site, and gp120-specific IgG MAbs in both nontransmitting and transmitting women.