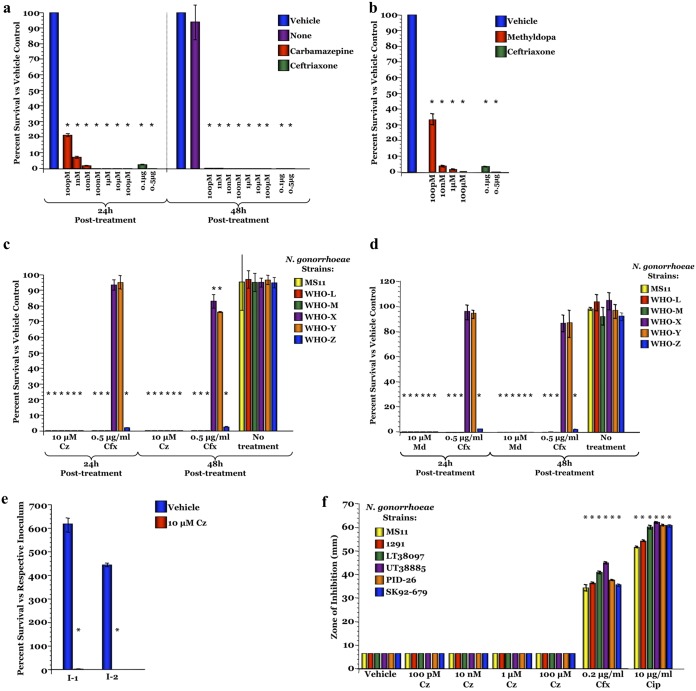
FIG 4.
Carbamazepine and methyldopa can cure N. gonorrhoeae infection of human cervical cells. To determine the potential utility of carbamazepine (Cz) and methyldopa (Md) in treating gonococcal cervicitis, Pex cells were infected with the noted strain of N. gonorrhoeae and cure assays were performed. Carbamazepine (a) and methyldopa (b) treatment resulted in dose-dependent reductions in N. gonorrhoeae strain MS11 survival at 24 h posttreatment, which was further reduced by 48 h (b). Carbamazepine (c) and methyldopa (d) were also effective against a panel of multidrug-resistant N. gonorrhoeae isolates. In this regard, both drugs were more effective than ceftriaxone (Cfx), the current recommended therapy, in treating multidrug-resistant gonococci. (e) Bacteria harvested from a 24-h infection (I-1) did not develop carbamazepine-resistance, in that 100% killing occurred when these bacteria were used in a second sequential infection (I-2) and treated with carbamazepine. (f) Well diffusion assays showed that carbamazepine had no effect on the N. gonorrhoeae strains tested in the absence of human cells. Each assay was performed in triplicates on 3 separate occasions. Data are presented as the means and variances of the average values obtained for each assay. *, P ≤ 0.0001 versus vehicle control; Cip, ciprofloxacin.