FIG 7.
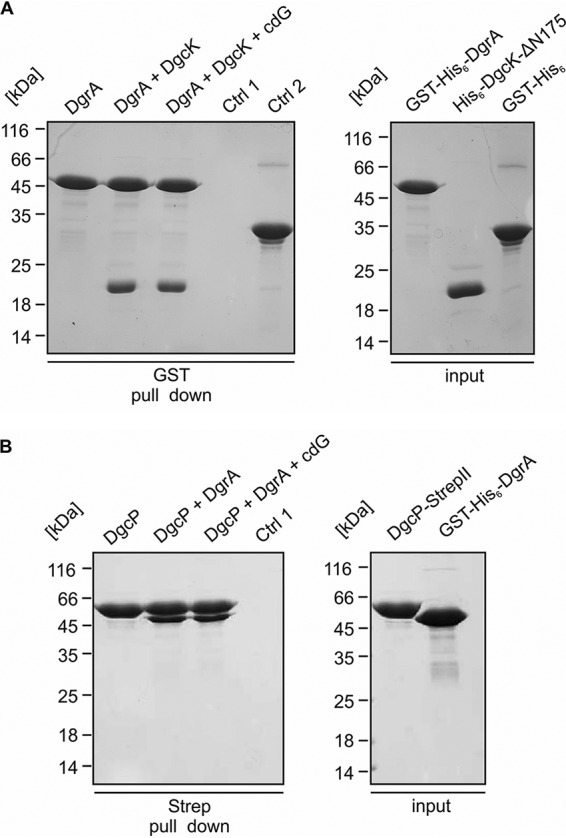
Interaction of the PilZ protein DgrA with DgcK and DgcP. (A, left) In vitro interaction analysis of GST-His6-DgrA and His6-DgcK-ΔN175. Coomassie blue-stained SDS-PAGE gel from a pulldown assay employing GST-His6-DgrA (bait), His6-DgcK-ΔN175 (prey), and GST (control [Ctrl]). Two nmol of GST-His6-DgrA was immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads (first lane), followed by incubation with 20 nmol His6-DgcK-ΔN175 (second lane) and 2 mM c-di-GMP (cdG) (third lane). Control 1 (fourth lane) is His6-DgcK-ΔN175, which does not bind to glutathione-Sepharose beads. Control 2 (fifth lane) is His6-DgcK-ΔN175, which does not bind the affinity tag GST. (A, right) Input controls for: GST-His-DgrA (first lane), His-DgcK-ΔN175 (second lane), GST-His6 (third lane). (B, left) In vitro interaction analysis of DgcP-Strep and GST-His6-DgrA. Coomassie blue-stained SDS-PAGE gel from a pulldown assay employing DgcP-StrepII (bait) and GST-His6-DgrA (prey). Two nmol of DgcP-StrepII was immobilized on Strep-Sepharose beads (first lane), followed by incubation with 20 nmol GST-His6-DgrA (second lane), which shows that DgcP-StrepII can immobilize GST-His6-DgrA on Strep-Sepharose. In the third lane, 2 nmol DgcP-Strep was immobilized on Strep-Sepharose beads, followed by incubation with 20 nmol GST-His6-DgrA and of 2 mM c-di-GMP. Control 1 (fourth lane) was GST-His6-DgrA, which does not bind to Strep-Sepharose beads. (B, right) Input controls for DgcP-StrepII (first lane), GST-His6-DgrA (second lane).
