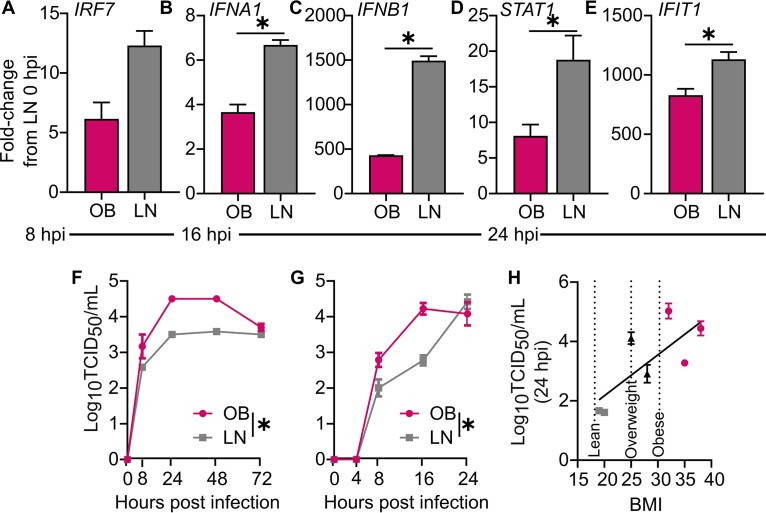
FIG 7.
Human primary respiratory epithelial cells from obese donors show increased influenza virus replication and blunted interferon responses. (A to E) RNA extracted from obese and lean host-derived NHBE cells (n = 3 wells/time point) infected at an MOI of 10 with CA/09 virus. Shown are gene expression normalized to that of GAPDH and average expression of target genes in lean cells at baseline. Compared to lean host-derived cells, obese host-derived NHBE cells had reduced expression of IRF7 at hour 8 p.i. (A), IFNA1 (B) and IFNB1 (C) at hour 16 p.i., and STAT1 (D) and IFIT1 (E) at hour 24 p.i. (F to H) Obese host-derived NHBE cells (n = 12 wells/donor) inoculated with CA/09 virus showed increased replication kinetics compared to those of lean host-derived cells. (F and G) Representative age-, race-, and sex-matched, BMI-discordant NHBE cells infected at an MOI of 0.01 with CA/09 virus (F) and MOI of 10 with CA/09 virus (G). Lean cells were derived from a 52-year-old white male with a BMI of 25, and obese cells derived from a 53-year-old white male with a BMI of 38. (H) Viral titers at hour 24 p.i. from a panel of BMI-discordant NHBE cells (n = 3 wells/donor; R2=0.4708). Data were analyzed for panels A to E with unpaired t test, for panels F and G with ordinary one-way ANOVA, and for panel H with linear regression. Data are represented as means ± standard errors (*, P < 0.05).