Figure 4.
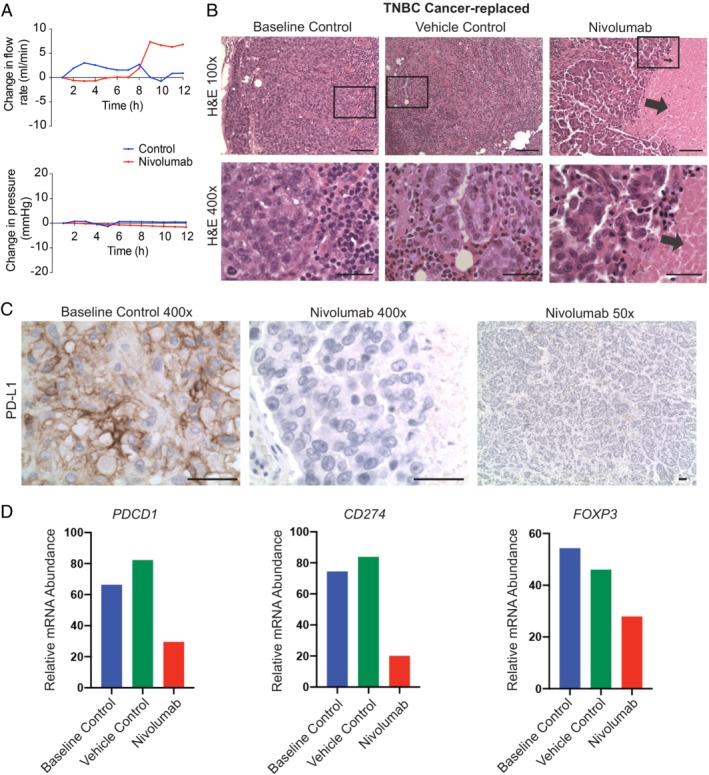
Nivolumab induced cancer cell death in a cancer‐replaced axillary lymph node (ALN). (A) Nivolumab infusion (1 μg over 60 min) resulted in an increased flow rate through an ALN from a patient with triple‐negative breast cancer (not seen in the vehicle control). (B) Histological cancer cell necrosis was observed in the nivolumab‐treated ALN (arrows), but not in the vehicle (normal saline) or baseline control ALN (fixed at time‐point 0; scale bars: 50 μm). (C) All tumour cells in the baseline control ALN were positive for PD‐L1. The nivolumab‐treated ALN was completely negative (scale bars: 50 μm). (D) NanoString IO360 analysis showed that PDCD1 (PD‐1), CD274 (PD‐L1), and FOXP3 transcript were down‐regulated in the nivolumab‐treated node compared with both control ALNs.
