Figure 1.
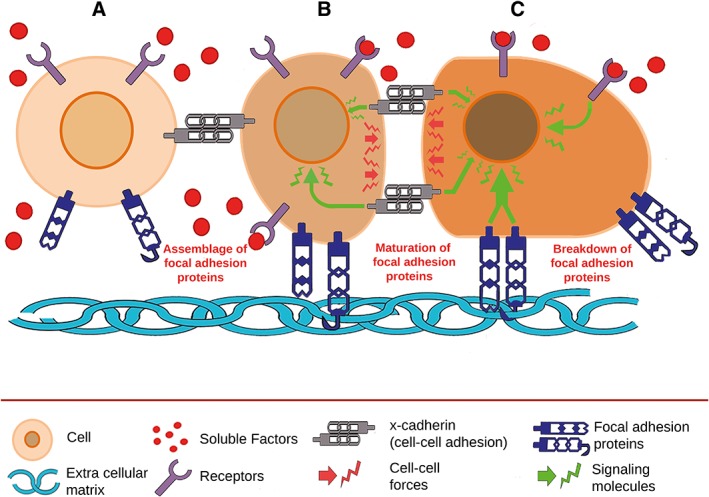
Schematic illustration of the formation and remodeling of focal adhesions.The dynamic process of focal adhesion is influenced by factors such as intercellular adhesion and morphogens. (A) At initial contact of the cells, focal adhesions assemble resulting in binding to specific adhesive motives in the extracellular matrix. (B) Focal and intercellular adhesions are increased, leading to a variety of cellular responses. Pertinent signal transduction pathways are upregulated, in particular, those involved in migratory processes as illustrated by changes in morphology and alignment. These signal transduction pathways may also allow the cell to present specific receptors that bind to corresponding ligands. (C) The concerted effect of all components allows controlled maturation and breakdown of focal adhesions resulting in coincident and coordinated movement of cells along the extracellular matrix. Color differences represent upregulation of processes in the nucleus and cytoplasm.
