Figure 1.
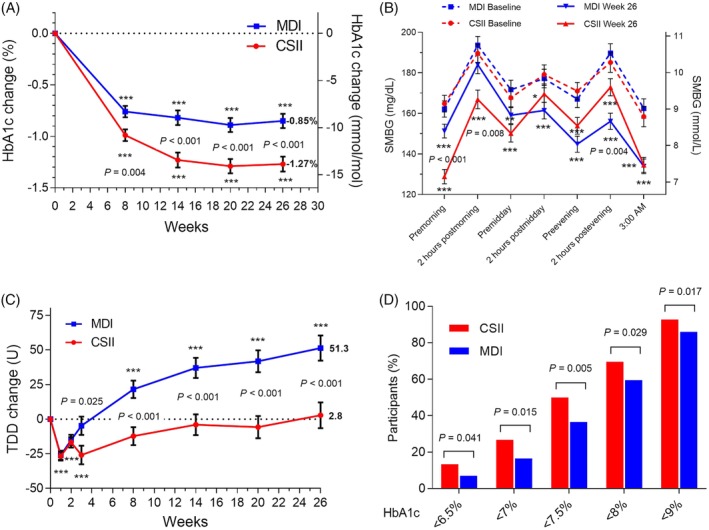
Selected outcome measures, all randomized participants by treatment (continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion [CSII], n = 209; multiple daily injections [MDI], n = 211). (A) Change from baseline in HbA1c. Data are LS mean ± SE; ***P <0.001 for change from baseline; P‐values are given for significant differences between treatments. (B) Seven‐point self‐monitored blood glucose (SMBG) profile at baseline and week 26. Only participants with a non‐missing baseline value and at least one non‐missing postbaseline SMBG value were included in analysis (CSII, n = 163; MDI, n = 174). *P <0.05, **P <0.01, ***P <0.001 for change from baseline; P‐values are given for significant differences between treatments. (C) Change from baseline in total daily insulin dose (TDD). Data are LS mean ± SE; ***P <0.001 for change from baseline; P‐values are given for significant differences between treatments. (D) Percentage of participants reaching HbA1c targets at 26 weeks by treatment; P‐values are given for significant differences between treatments
