Figure 6.
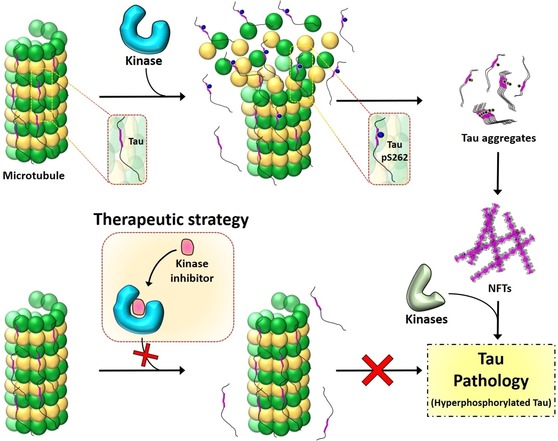
The residue S262 plays a vital role in stabilizing the binding of tau to tubulin of MTs. Phosphorylation at S262 disrupts the tau–MT interaction (top), leading to tau accumulation and pathology formation. Inhibiting the phosphorylation at S262 or other sites that directly or indirectly disrupt the tau–MT interaction by targeting the kinases involved could be an effective therapeutic strategy (bottom) to prevent tau dissociation from MTs by stabilizing the native state of the tau–tubulin complex.
