Table 2.
Reactivity of amoxicillin (AX) with thiol (protected, reduced or oxidized forms) and nonthiol antioxidants.
| Compound | Formed products | Remaining | Other products (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DKP (%) | AXO (%) | AX (%) | |||
| None | 9 | 9 | 82 | ||
| DTT |
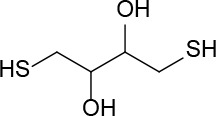
|
50 | 9 | 41 | – |
| N-acetyl-cysteine |
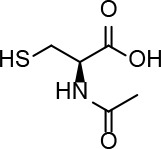
|
27 | 8 | 65 | – |
| L-cysteine |
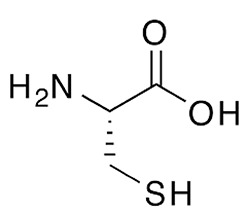
|
2 | 12 | 0 | 86 (Amoxicilloyl-Cys conjugate) |
| L-Glutathione reduced (GSH) |
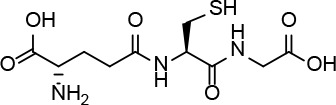
|
29 | 8 | 63 | – |
| L-Glutathione oxidized (GSSG) |
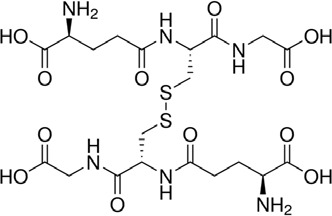
|
9 | 9 | 82 | – |
| S-para-nitro-benzyl glutathione |
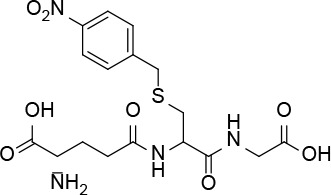
|
9 | 9 | 82 | – |
| Trolox |
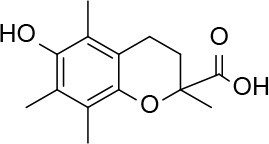
|
9 | 9 | 82 | – |
| TCEP |
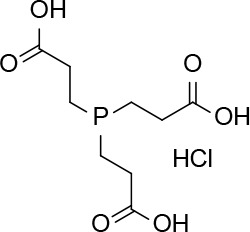
|
20 | 10 | 20 | 50 (related nonidentified amoxicilloyl products) |
Incubations were carried out using equimolar amounts of AX and the thiol functional-reagent or nonthiol antioxidant, in phosphate buffer saline (PBS) at 37°C for 24 h and lyophilized. Integration of 1H-NMR signals was employed for calculating the quantity of obtained products.
